Overview
GMP experience encompasses the practical knowledge and skills that professionals in the life sciences acquire regarding Good Manufacturing Practices. These practices are vital for ensuring product quality and regulatory compliance in pharmaceutical manufacturing. As regulations evolve, the significance of this experience grows, necessitating robust management systems.
Case studies illustrate that companies prioritizing GMP practices can significantly reduce compliance issues and enhance operational efficiency. Therefore, investing in GMP experience is not merely beneficial; it is essential for maintaining a competitive edge in the industry.
Introduction
Understanding Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) is essential for professionals in the life sciences, as these guidelines form the backbone of product safety and regulatory compliance. As the pharmaceutical landscape evolves, the demand for individuals with robust GMP experience has surged, particularly in light of increasing scrutiny from regulatory bodies and the complexities introduced by modern manufacturing technologies.
However, what does it truly mean to possess GMP experience? How can it significantly influence the quality and safety of pharmaceutical products? This article delves into the critical components of GMP experience, its historical significance, and real-world applications that underscore its importance in safeguarding public health and enhancing operational excellence in the industry.
Define GMP Experience in Life Sciences
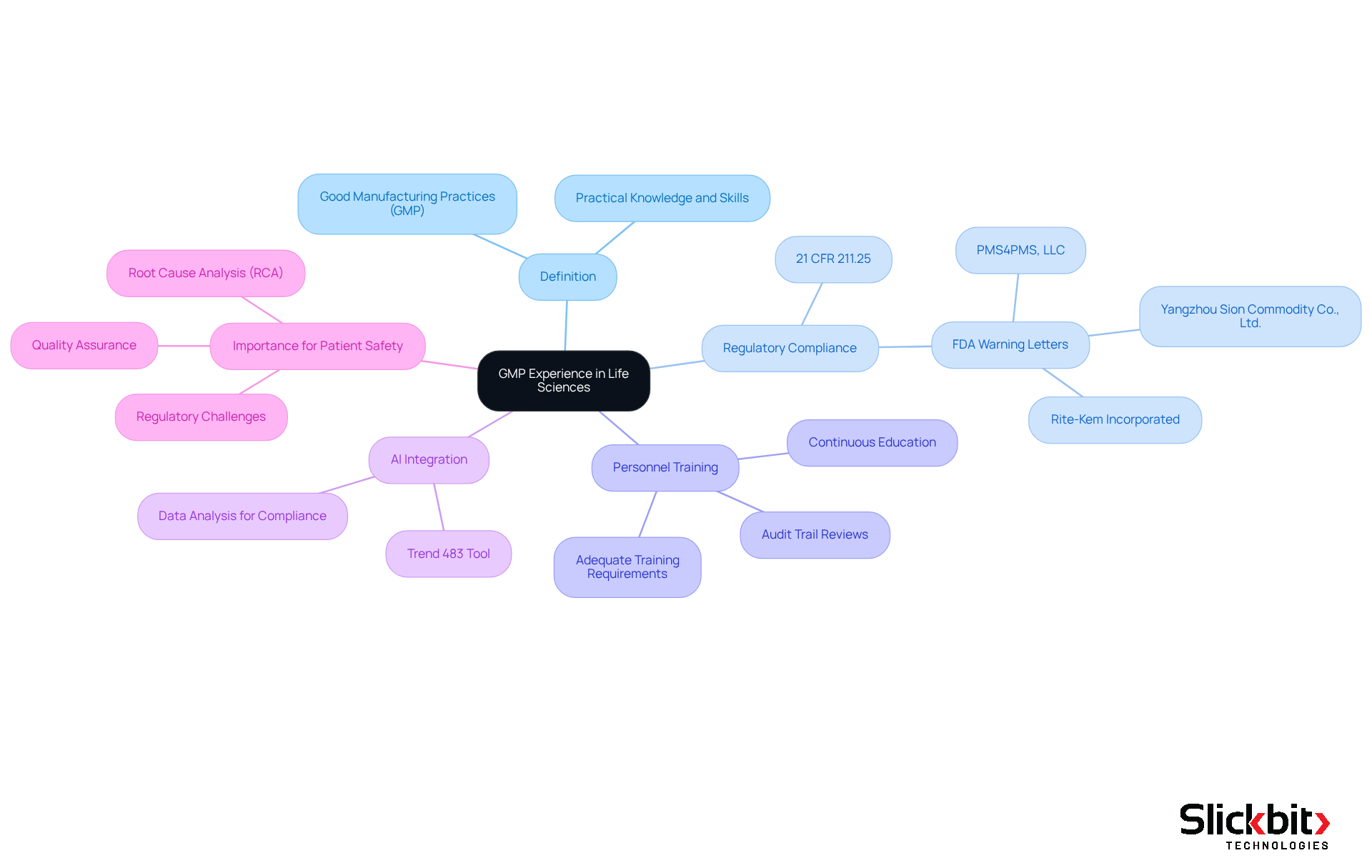
What is GMP experience, and how does it embody the practical knowledge and skills that professionals in the life sciences sector acquire regarding Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP)? These practices are governed by a comprehensive collection of rules and guidelines designed to ensure that products are consistently manufactured and managed according to stringent standards. This expertise is crucial for individuals engaged in manufacturing, quality assurance, and regulatory compliance within pharmaceutical companies, biotech firms, and contract research organizations (CROs).
As we approach 2025, understanding what is GMP experience has become increasingly evident. Numerous FDA Warning Letters have highlighted persistent deficiencies in personnel training and adherence to 21 CFR 211.25, which raises concerns about what is GMP experience for individuals involved in drug product manufacturing, as they must possess appropriate education, training, and experience.
Moreover, the evolving regulatory landscape necessitates that pharmaceutical experts not only implement GMP practices effectively but also stay informed about the latest guidelines and compliance standards. This includes a thorough understanding of audit trail evaluations and Root Cause Analysis (RCA), which are essential for addressing regulatory challenges and ensuring product quality. The integration of AI tools, such as Trend 483, significantly enhances this process by identifying trends in systemic risks and compliance from FDA inspections, thereby facilitating informed decision-making and proactive management of GMP standards. Trend 483 empowers users to search, filter, and analyze complete 483s for deeper insights, which are vital for maintaining adherence. As the industry continues to navigate new challenges, the expertise of seasoned professionals in upholding GMP standards will be critical in protecting patient safety and ensuring regulatory compliance.
Explore the Historical Context and Importance of GMP
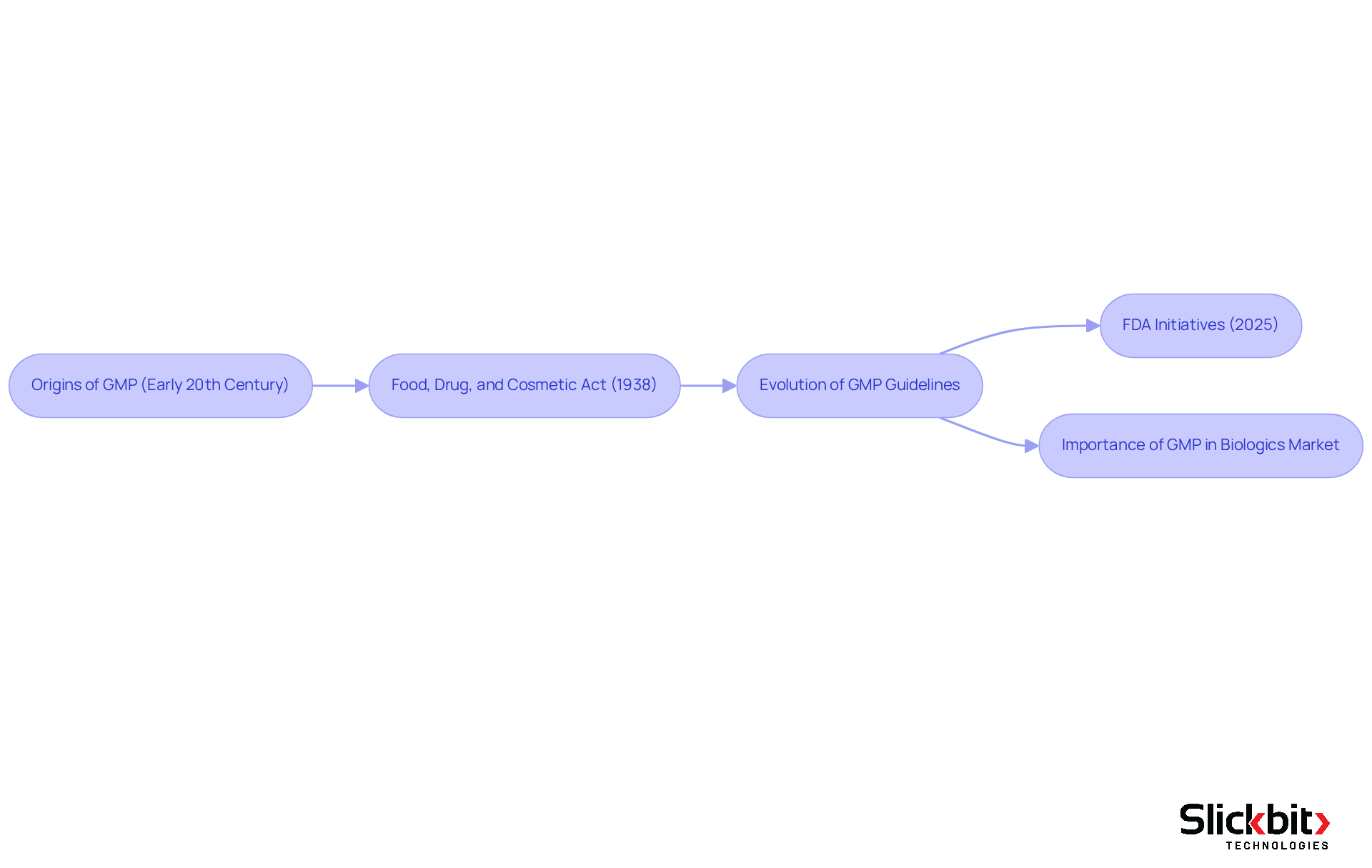
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) emerged as a critical response to public health emergencies, emphasizing the necessity for stringent control within the pharmaceutical sector. The origins of GMP can be traced back to the early 20th century, gaining momentum with the enactment of the Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act in 1938. This landmark legislation mandated inspections of manufacturing facilities, establishing a foundation for regulatory oversight and accountability. Over the years, GMP guidelines have evolved significantly, with the FDA and other regulatory bodies continuously updating standards to address the challenges posed by modern drug manufacturing.
For instance, the FDA's recent initiatives in 2025 aim to align GMP regulations, showcasing a steadfast commitment to enhancing product safety and standards. Understanding what is GMP experience is crucial, as it underscores the importance of preventing contamination, ensuring product consistency, and safeguarding consumer health, thereby fostering trust in pharmaceutical products. Case studies illustrate the impact of these regulations, such as the FDA's emphasis on comprehensive training programs, recognized as essential for compliance and assurance.
As the biologics market continues to expand, projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 15% until 2027, the relevance of robust GMP practices becomes increasingly vital in upholding industry standards and public confidence.
Identify Key Characteristics and Components of GMP Experience
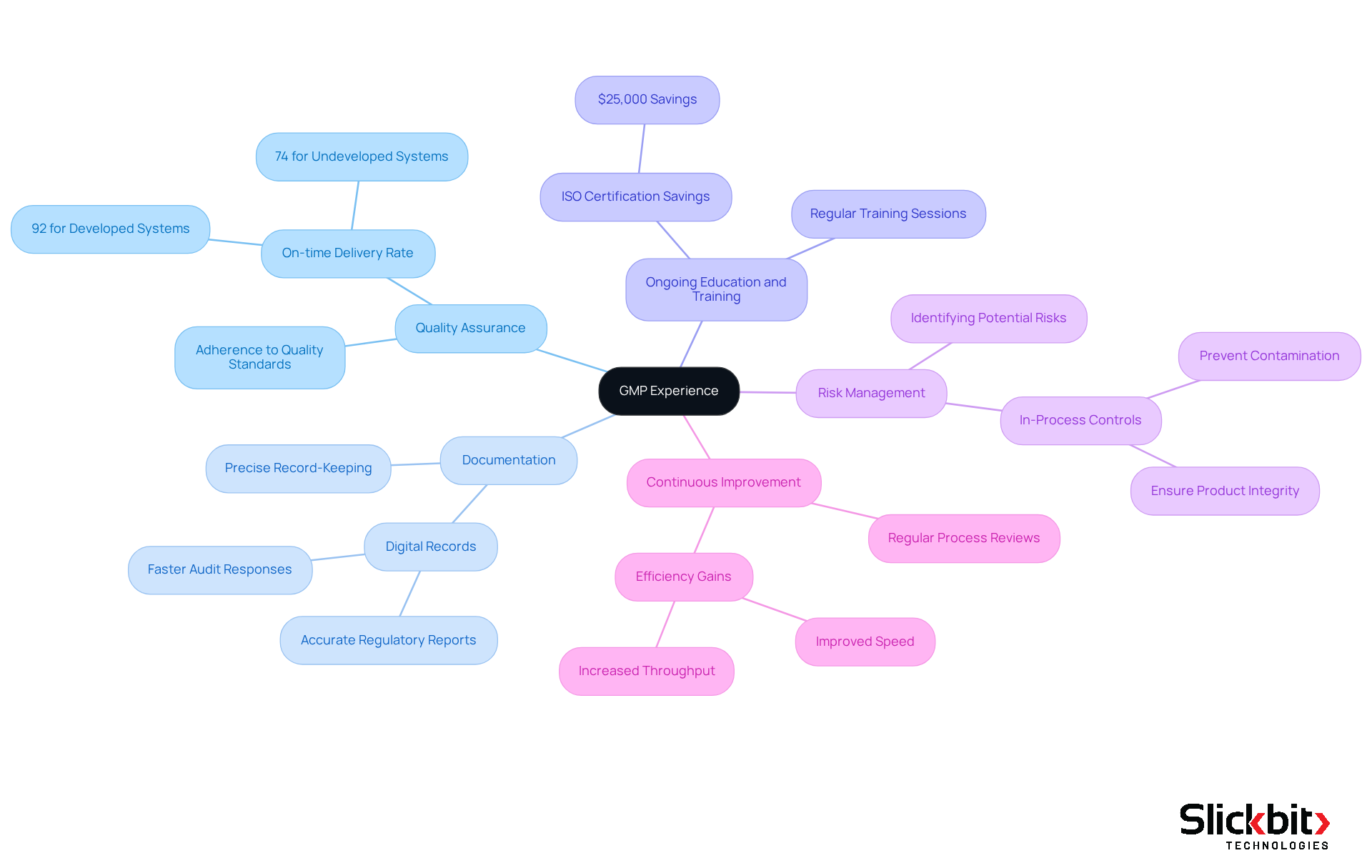
What is GMP experience includes key characteristics such as a profound understanding of management systems, regulatory requirements, and the effective implementation of standard operating procedures (SOPs). Essential components of GMP experience include:
-
Quality Assurance: This aspect ensures that all processes adhere to established quality standards, thereby guaranteeing that products are consistently safe and effective. Notably, businesses with developed management systems report an impressive on-time delivery rate of 92%, significantly higher than the 74% observed in those lacking such systems.
-
Documentation: Precise record-keeping of manufacturing processes, quality control tests, and regulatory audits is crucial. The use of digital records facilitates quicker responses to audits and provides accurate regulatory reports, aligning with FDA guidelines that emphasize the importance of electronic record-keeping.
-
Ongoing education and training for staff are vital to ensure adherence to what is GMP experience. Organizations that understand what is GMP experience through regular training sessions can achieve substantial improvements in compliance, with those attaining ISO 9001 or ISO 13485 certification reporting savings of at least $25,000 within a year.
-
Risk Management: Identifying potential risks in the manufacturing process and implementing strategies to mitigate them is essential. The FDA's draft guidance underscores the importance of in-process controls and testing to prevent contamination and ensure product integrity.
-
Continuous Improvement: Engaging in regular reviews and updates of processes enhances efficiency and adherence to standards. Organizations that invest in effective management practices not only ensure reliable supply and fewer defects but also achieve efficiency gains, such as improved speed and throughput.
By concentrating on these elements, R&D managers can cultivate a culture of excellence and compliance, ultimately leading to improved product outcomes and increased operational efficiency.
Examine Real-World Examples of GMP Experience Implementation
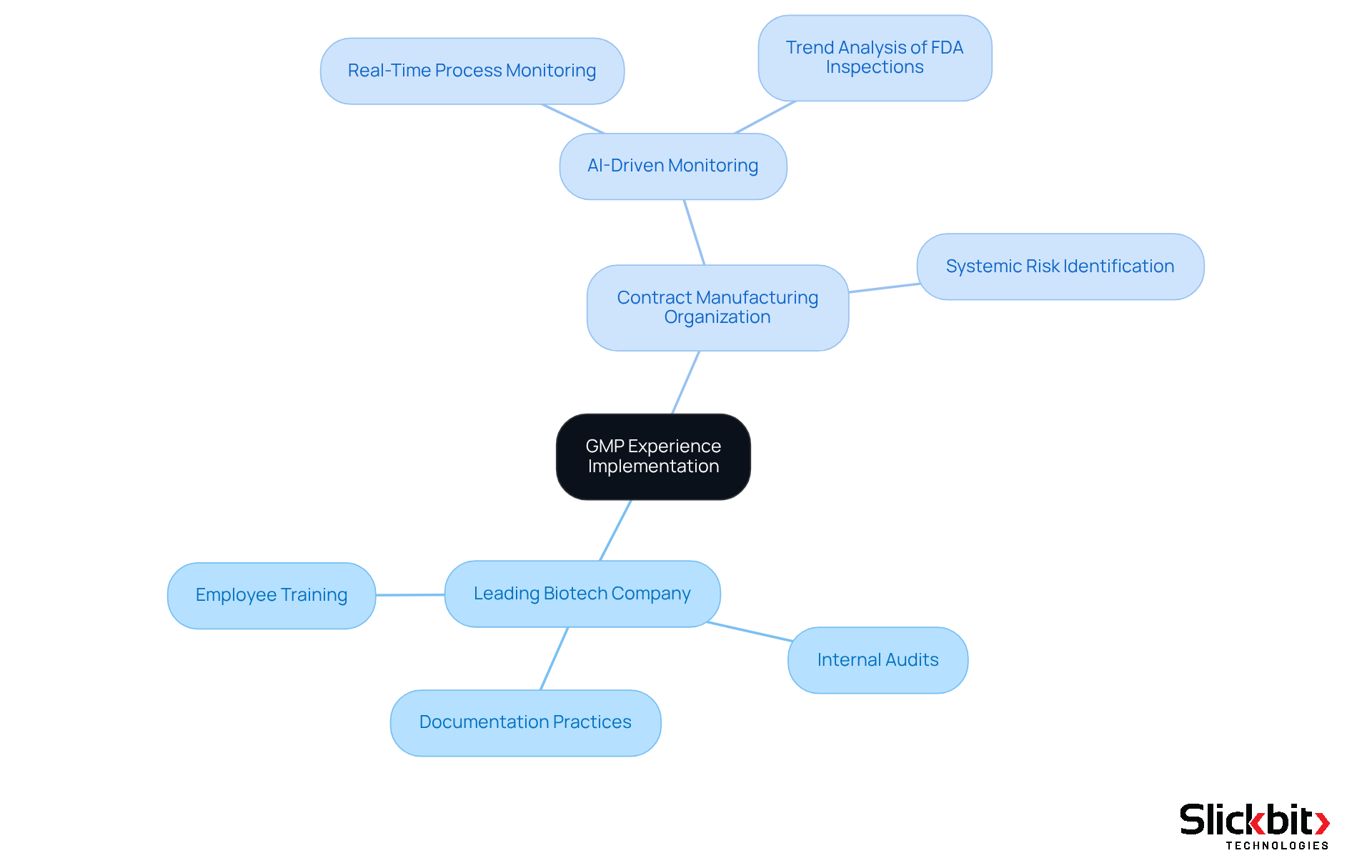
Real-world instances of GMP experience application illustrate how pharmaceutical firms adeptly navigate regulatory inspections while upholding high product standards. A notable example is a leading biotech company that established a robust management system encompassing comprehensive employee training, meticulous documentation practices, and regular internal audits. This proactive approach not only ensured compliance with FDA regulations but also resulted in a significant reduction in product recalls, averaging 1,284 annually since 2012 due to GMP non-compliance.
Another compelling case involves a contract manufacturing organization (CMO) that has integrated advanced technologies, including AI-driven tools, for real-time monitoring of production processes. This innovation has markedly improved their ability to maintain GMP standards and promptly address any deviations, thereby minimizing the risk of quality-related issues. By leveraging AI to analyze trends in FDA inspections and utilizing features such as searching and filtering FDA 483s, these organizations can pinpoint systemic risks and recurring violations, further enhancing their compliance efforts.
These examples underscore the crucial role of what is GMP experience in cultivating a culture of quality and adherence within the life sciences sector, which ultimately contributes to enhanced patient safety and a reduction in adverse events, exceeding 22 million reports since 2012. By prioritizing GMP practices and employing AI for regulatory insights, companies not only meet legal obligations but also boost their operational efficiency and market competitiveness. Furthermore, the FDA categorizes drug recalls into three classes, highlighting the seriousness of compliance issues and the imperative nature of maintaining GMP standards. As articulated by the FDA, "A recall is defined as a firm’s removal or correction of a distributed product that the FDA deems is in violation of its laws," emphasizing the significance of effective GMP practices. Additionally, the case of White Raven achieving GMP certification in just 18 months exemplifies the successful implementation of GMP practices, further showcasing what is GMP experience and its tangible benefits in biotech firms.
Conclusion
Understanding GMP experience is fundamental for professionals in the life sciences, particularly within the pharmaceutical and biotech sectors. This expertise encompasses the essential knowledge and practical skills necessary to navigate the complexities of Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), which are vital for ensuring product quality and regulatory compliance. As the industry evolves, the significance of possessing a robust GMP experience cannot be overstated; it directly impacts patient safety and the integrity of drug manufacturing processes.
The article highlights several key aspects of GMP experience, including:
- Historical context
- Essential characteristics
- Real-world applications
It emphasizes the importance of:
- Quality assurance
- Documentation
- Continuous education
- Risk management
- A culture of continuous improvement
These components collectively foster an environment where compliance with stringent regulatory standards is not only achievable but also sustainable. Furthermore, the integration of advanced technologies, such as AI tools, has proven invaluable in enhancing GMP adherence and facilitating proactive management of potential compliance issues.
In conclusion, the insights presented underscore the critical role that GMP experience plays in the pharmaceutical industry. As the landscape continues to change, it is imperative for R&D managers and professionals to prioritize and invest in developing this expertise. By doing so, they not only ensure compliance with evolving regulations but also contribute to the broader goal of safeguarding public health. Embracing GMP practices is not merely a regulatory obligation; it is a commitment to excellence that ultimately enhances product quality, operational efficiency, and consumer trust in pharmaceutical products.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is GMP experience in the life sciences sector?
GMP experience refers to the practical knowledge and skills that professionals acquire regarding Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). It encompasses a comprehensive understanding of the rules and guidelines designed to ensure consistent manufacturing and management of products according to stringent standards.
Why is GMP experience important for professionals in pharmaceutical companies and biotech firms?
GMP experience is crucial for individuals engaged in manufacturing, quality assurance, and regulatory compliance, as it ensures that they possess the necessary education, training, and experience to adhere to industry standards and regulations.
What recent trends have highlighted the importance of GMP experience?
Numerous FDA Warning Letters have pointed out deficiencies in personnel training and adherence to regulations, particularly 21 CFR 211.25, emphasizing the need for professionals involved in drug product manufacturing to have appropriate GMP experience.
What additional knowledge is required for professionals regarding GMP practices?
Professionals must stay informed about the latest guidelines and compliance standards, including a thorough understanding of audit trail evaluations and Root Cause Analysis (RCA) to address regulatory challenges and ensure product quality.
How do AI tools like Trend 483 assist in GMP compliance?
AI tools such as Trend 483 help identify trends in systemic risks and compliance issues from FDA inspections, allowing users to search, filter, and analyze complete 483s for deeper insights, which are essential for maintaining adherence to GMP standards.
What is the significance of maintaining GMP standards in the life sciences industry?
Upholding GMP standards is critical for protecting patient safety and ensuring regulatory compliance as the industry navigates new challenges and evolving regulations.




