Overview
This article delves into the comprehensive significance of Quality Management Systems (QMS) within pharmaceutical research and development. It highlights critical components such as:
- Document control
- Quality assurance
- Risk management
- Continuous improvement
All of which are vital for upholding product quality and ensuring regulatory compliance. Furthermore, it elucidates how these elements synergistically enhance operational effectiveness, mitigate risks, and guarantee adherence to established standards. Consequently, this integration not only leads to superior product excellence but also fosters heightened customer satisfaction.
Introduction
A robust Quality Management System (QMS) is pivotal in the pharmaceutical R&D landscape, serving as the backbone for ensuring product quality and regulatory compliance. Understanding the full implications of QMS enables R&D managers to leverage essential components—such as document control, risk management, and continuous improvement—to enhance operational efficiency and product excellence. However, a significant challenge persists: how can organizations effectively implement these systems to not only meet regulatory standards but also cultivate a culture of innovation and accountability? This inquiry is critical for fostering an environment where quality and compliance coexist with creativity and progress.
Define Quality Management Systems in Pharmaceutical R&D
A Quality Management System (QMS) in pharmaceutical R&D illustrates the qms full meaning by serving as an organized framework that encompasses all methods, procedures, and responsibilities aimed at ensuring product quality and compliance with regulatory standards. This system integrates critical elements such as documentation, process control, and continuous improvement, facilitating the delivery of high-quality pharmaceutical products. By implementing a clearly articulated QMS, organizations can uphold consistency in their operations, thereby minimizing the risk of errors and enhancing overall product standards.
According to the FDA, the qms full meaning is essential for overseeing standards throughout the product lifecycle—from development to manufacturing and distribution. Furthermore, the integration of AI technologies, such as those utilized in Trend 483, significantly enhances adherence by identifying patterns in systemic risks and recurring infractions from FDA inspections. Trend 483 empowers users to search, filter, and access complete 483s for deeper insights, supporting regulatory compliance and fostering a culture of excellence within the organization. Consequently, this approach streamlines operations and boosts overall efficiency.
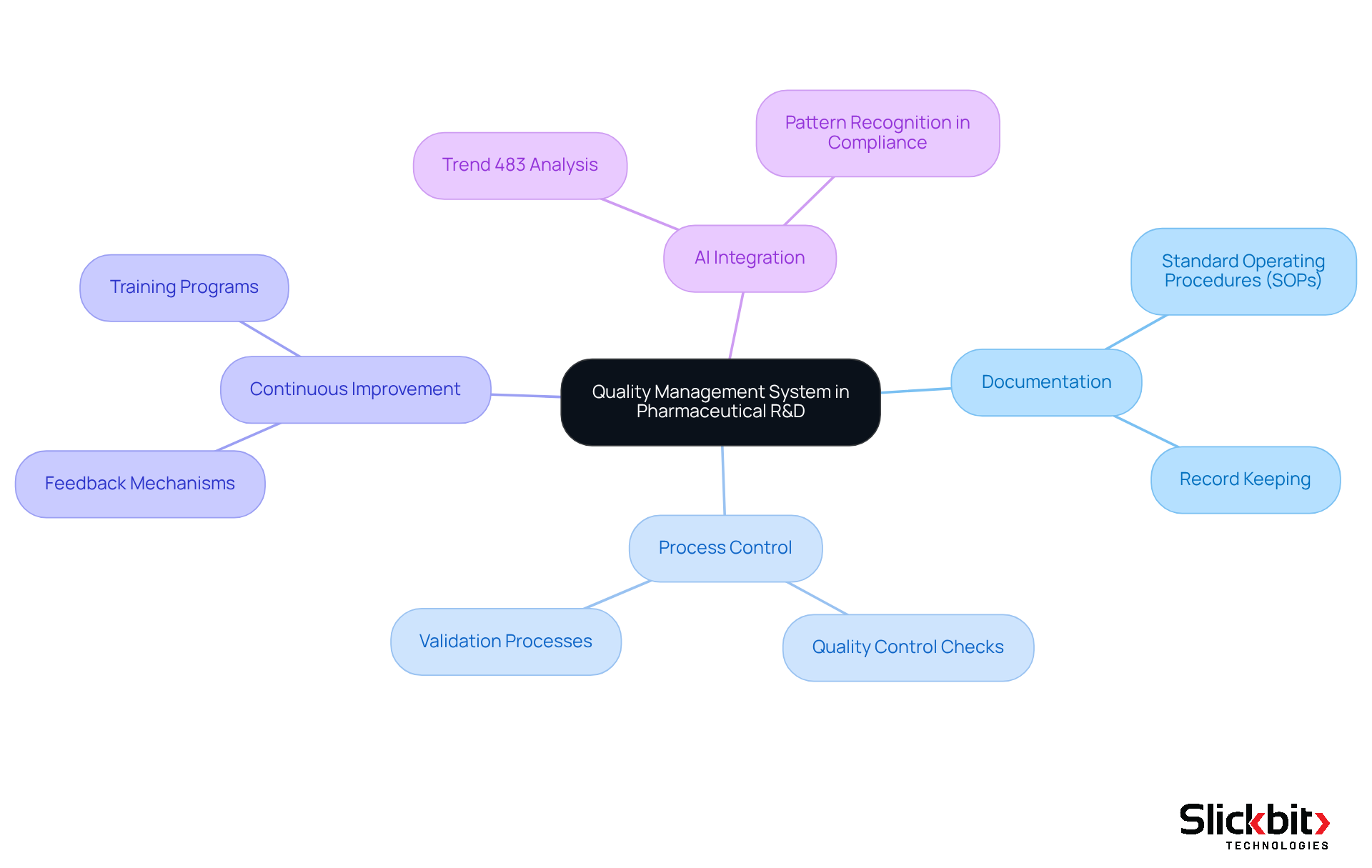
Identify Key Elements of an Effective QMS
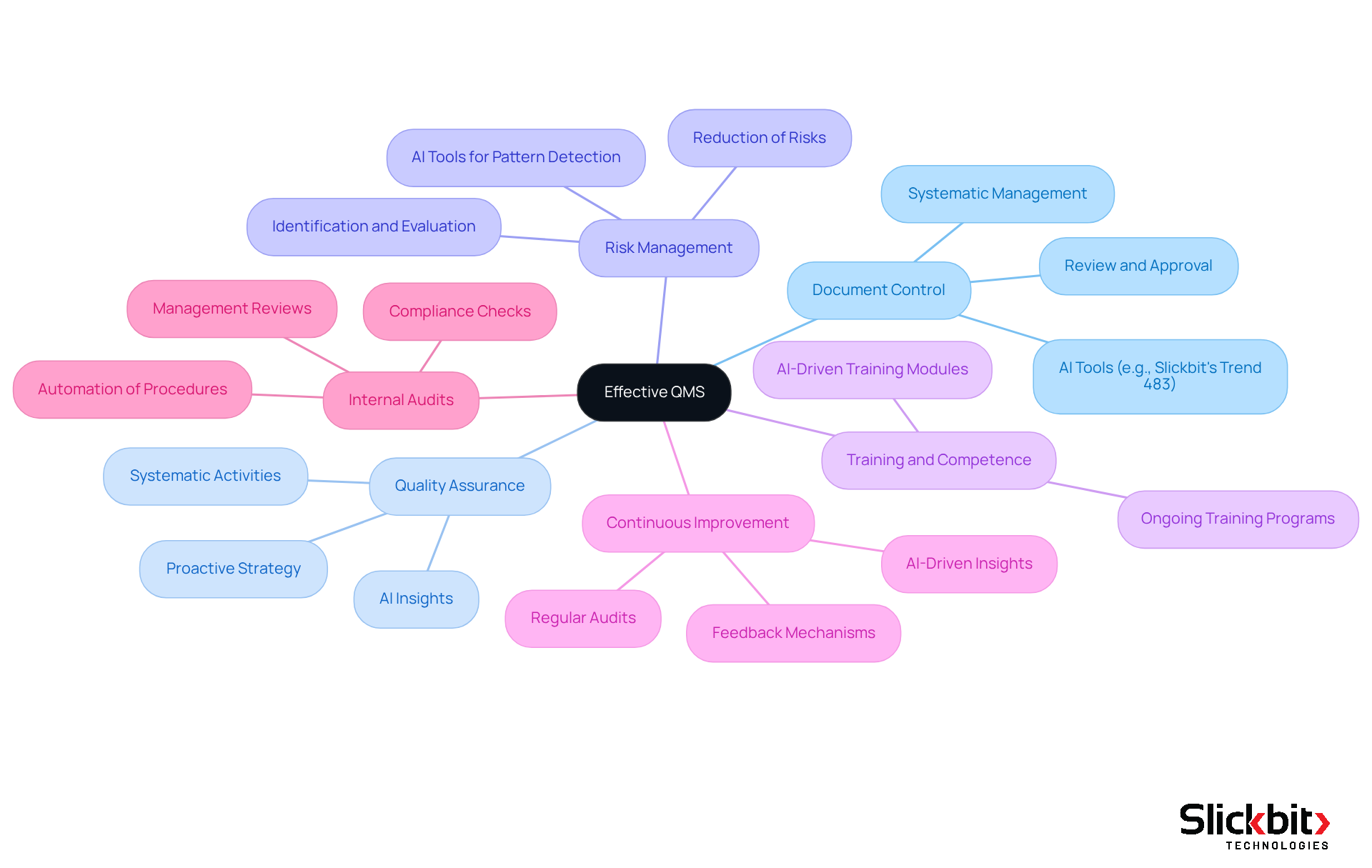
An effective Quality Management System (QMS) is essential for maintaining high standards in pharmaceutical R&D, particularly in document control, where understanding the QMS full meaning is crucial. The backbone of a QMS is Document Control, which ensures that all documents are systematically managed, reviewed, and approved. Proper document control is vital for maintaining accuracy and compliance, crucial for meeting regulatory standards. A well-organized document control system typically includes a manual, policies, standard operating procedures (SOPs), work instructions, and records, all arranged for easy access and traceability. Furthermore, AI tools like Slickbit's Trend 483 enhance document control by enabling users to efficiently search and filter documents, ensuring that the most relevant information is readily available.
Quality Assurance involves systematic activities designed to ensure that quality requirements are consistently met throughout the product lifecycle. By implementing quality assurance methods, organizations can create a proactive strategy for adherence and risk management. In addition, utilizing AI insights can streamline these processes by identifying potential compliance issues before they escalate. Concentrated on operational methods and actions, quality assurance guarantees that products fulfill standards through stringent testing and inspection protocols. AI can further aid in examining control data to identify trends and areas for enhancement.
Risk Management is a systematic strategy that identifies, evaluates, and reduces risks related to product standards and regulations, vital for maintaining the integrity of pharmaceutical products. Employing AI tools such as Slickbit's Trend 483 can significantly improve this approach by detecting patterns in systemic risks and recurring violations from FDA 483s, offering deeper insights into regulatory issues. The capability to view full 483s allows for a comprehensive understanding of past violations, informing future risk management strategies.
Training and competence are essential for effective QMS implementation, which is crucial to grasping the QMS full meaning. Ensuring that personnel are adequately trained and competent is crucial, and ongoing training programs help maintain high levels of quality and compliance. AI-driven training modules can personalize learning experiences based on individual performance metrics, enhancing the overall effectiveness of training initiatives.
The principle of Continuous Improvement entails establishing methods for ongoing assessment and enhancement of the QMS, enabling organizations to adapt to evolving regulations and market demands. Regular audits and feedback mechanisms are integral to this process. AI-driven insights can assist by highlighting areas for enhancement based on regulatory data, ensuring that organizations remain agile and responsive.
Conducting Internal Audits regularly helps ensure compliance and identify areas for improvement. These audits are crucial for maintaining high standards and addressing any nonconformities. Moreover, AI can automate audit procedures, making them more efficient and comprehensive. Periodic Management Reviews by management ensure that the QMS is effective and aligned with organizational goals. This review process is essential for accountability and strategic alignment, with AI tools providing management with real-time data and insights that enhance decision-making processes.
These elements work together to establish a robust framework that upholds excellence objectives and regulatory compliance in pharmaceutical R&D. By adopting optimal methods in document management and leveraging AI capabilities, organizations can improve traceability and efficiency, ultimately leading to enhanced product standards and patient safety.
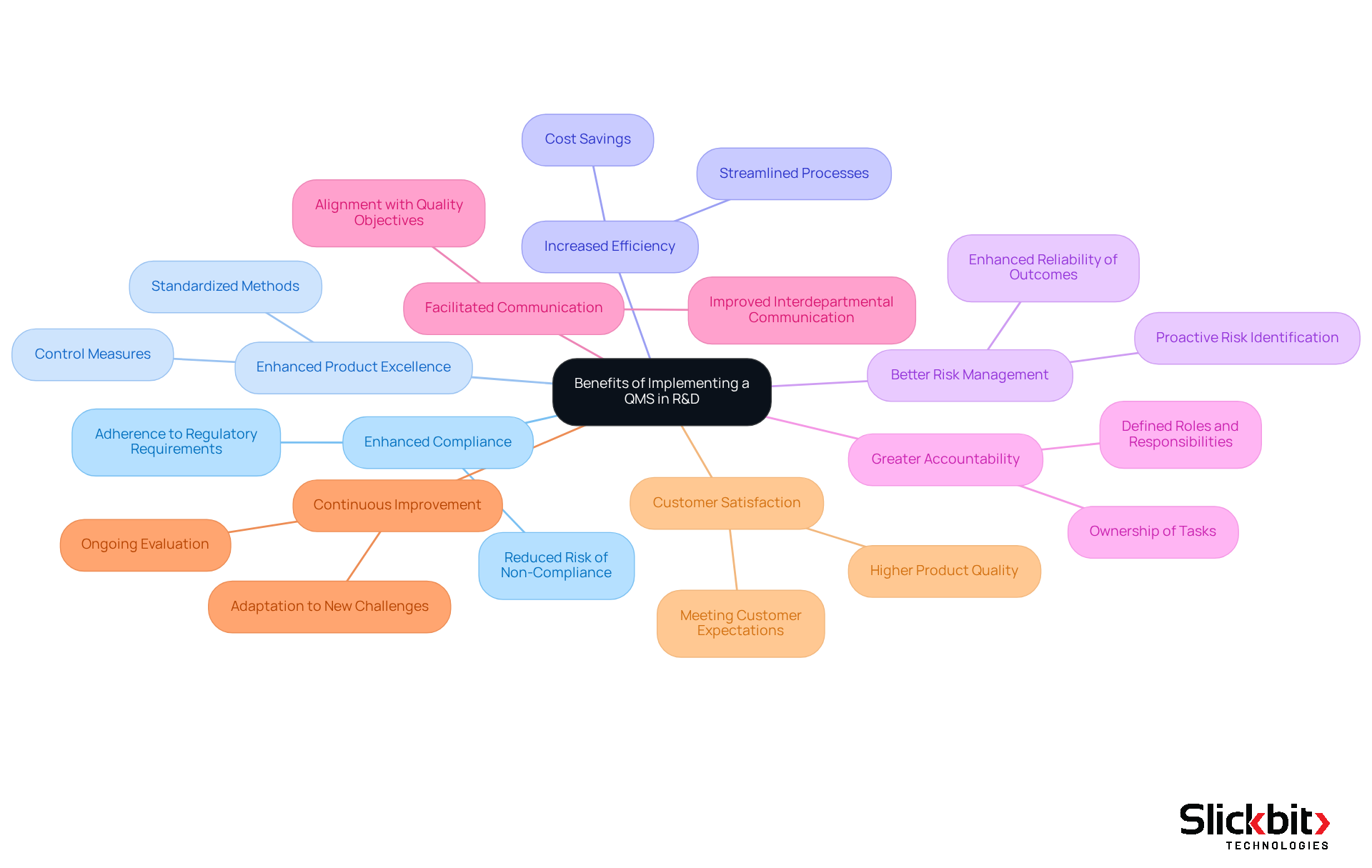
Explore Benefits of Implementing a QMS in R&D
Implementing a Quality Management System (QMS) in pharmaceutical R&D presents numerous advantages that can significantly enhance operational effectiveness, emphasizing the QMS full meaning.
-
Enhanced Compliance: A QMS ensures strict adherence to regulatory requirements, thereby reducing the risk of non-compliance and the associated penalties.
-
Enhanced Product Excellence: By standardizing methods and implementing control measures, organizations can consistently produce superior products that meet industry standards.
-
Increased Efficiency: Streamlined processes minimize waste and redundancies, resulting in faster project timelines and substantial cost savings.
-
Better Risk Management: A proactive approach to identifying and mitigating risks enhances the reliability of R&D outcomes, ensuring that projects are completed successfully.
-
Greater Accountability: Clearly defined roles and responsibilities within the QMS foster a culture of accountability among team members, promoting ownership of tasks.
-
Facilitated Communication: A structured framework improves communication across departments, ensuring alignment with quality objectives and enhancing collaboration.
-
Continuous Improvement: The QMS promotes a culture of ongoing evaluation and enhancement, allowing organizations to adapt to new challenges and seize opportunities for growth.
-
Customer Satisfaction: Ultimately, a robust QMS leads to higher customer satisfaction by ensuring that products consistently meet or exceed expectations.
By recognizing and leveraging these benefits, R&D managers can significantly enhance their operational effectiveness and contribute to the overall success of their organizations.
Conclusion
Implementing a Quality Management System (QMS) in pharmaceutical R&D is not merely essential; it is critical for ensuring product quality and regulatory compliance. By establishing a structured framework, organizations can effectively manage processes, enhance operational efficiency, and minimize risks associated with product development. The significance of a QMS transcends mere compliance; it embodies a commitment to excellence that drives continuous improvement and fosters a culture of accountability within teams.
This article highlights several key components that contribute to an effective QMS, including:
- Document control
- Quality assurance
- Risk management
- Training
- Continuous improvement
Each element plays a pivotal role in maintaining high standards and ensuring that all products meet regulatory requirements. Furthermore, the integration of AI technologies significantly enhances these processes, allowing for more efficient audits, better risk assessments, and improved training methodologies. By leveraging these insights, R&D managers can optimize their operations and significantly reduce the likelihood of compliance issues.
In conclusion, the implementation of a robust QMS is not just a regulatory necessity; it is a strategic advantage for pharmaceutical R&D teams. Embracing the full meaning of Quality Management Systems can lead to enhanced product quality, greater operational efficiency, and ultimately, increased customer satisfaction. R&D managers are strongly encouraged to prioritize the establishment of a comprehensive QMS, recognizing its potential to drive success and innovation in an increasingly complex regulatory landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Quality Management System (QMS) in pharmaceutical R&D?
A Quality Management System (QMS) in pharmaceutical R&D is an organized framework that includes methods, procedures, and responsibilities aimed at ensuring product quality and compliance with regulatory standards.
What are the key elements of a QMS?
Key elements of a QMS include documentation, process control, and continuous improvement, all of which facilitate the delivery of high-quality pharmaceutical products.
How does a QMS benefit organizations in pharmaceutical R&D?
Implementing a clearly articulated QMS helps organizations maintain consistency in their operations, minimizing the risk of errors and enhancing overall product standards.
Why is the QMS important according to the FDA?
The FDA emphasizes the importance of a QMS for overseeing standards throughout the product lifecycle, from development to manufacturing and distribution.
How do AI technologies enhance QMS in pharmaceutical R&D?
AI technologies, such as those used in Trend 483, enhance QMS by identifying patterns in systemic risks and recurring infractions from FDA inspections, thereby improving adherence to regulatory standards.
What is Trend 483 and how does it support regulatory compliance?
Trend 483 is a tool that allows users to search, filter, and access complete 483s for deeper insights, supporting regulatory compliance and fostering a culture of excellence within organizations.
What impact does a QMS have on operational efficiency?
A well-implemented QMS streamlines operations and boosts overall efficiency within pharmaceutical organizations.




