Overview
The full form of QMS in the pharmaceutical sector is a Quality Management System, which encompasses a comprehensive integration of policies, processes, and procedures designed to ensure product quality and regulatory compliance. This system is crucial, as it significantly mitigates risks associated with product failures, reduces the likelihood of recalls, and enhances operational efficiency. Consequently, a robust QMS not only safeguards public health but also improves business outcomes within the pharmaceutical industry. By implementing such a system, organizations can achieve a competitive edge while adhering to regulatory standards.
Introduction
In the intricate landscape of the pharmaceutical industry, the imperative of maintaining product quality and regulatory compliance cannot be overstated. The Quality Management System (QMS) stands as a crucial framework, ensuring not only adherence to rigorous standards but also fostering operational efficiency. As organizations confront the dual challenges of evolving regulations and shifting market demands, a pivotal question emerges: how can an effective QMS not only mitigate risks but also catalyze continuous improvement and innovation within pharmaceutical operations?
Define Quality Management System (QMS) in Pharma
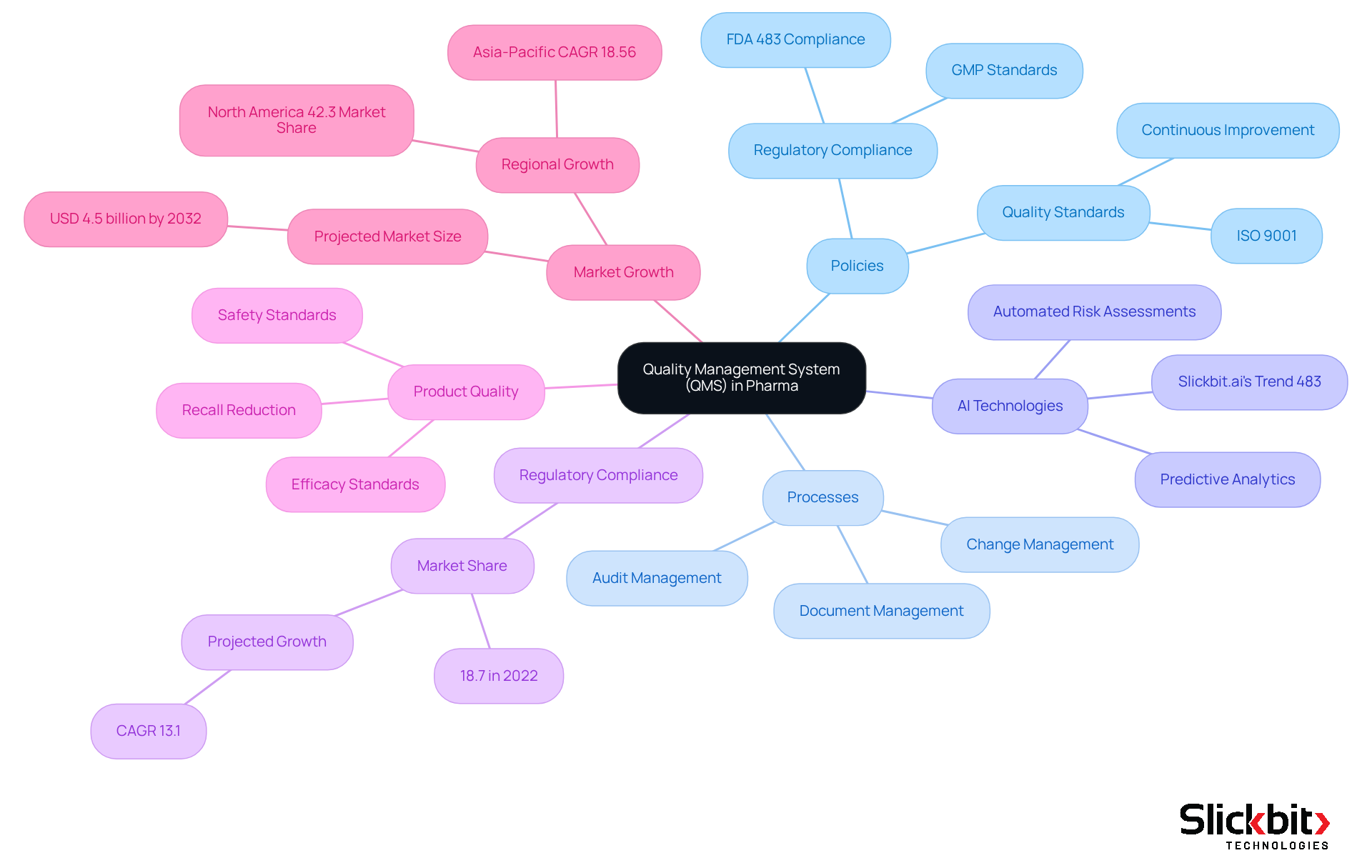
The QMS full form in pharma signifies a structured framework that integrates policies, processes, and procedures, ensuring consistent standards of excellence and adherence to regulatory requirements. This system encompasses various organizational functions, significantly enhancing product quality and operational efficiency. With the emergence of AI technologies, such as Slickbit.ai's Trend 483, pharmaceutical companies can leverage advanced tools to identify trends in systemic risks and regulatory concerns derived from FDA 483s, thereby improving their QMS. Specifically, Trend 483 analyzes FDA 483s to uncover patterns that inform risk management and regulatory strategies.
Implementing a robust QMS full form in pharma is crucial for effectively managing risks, maintaining compliance, and fostering continuous improvement within pharmaceutical companies. It plays a vital role in ensuring that products meet safety and efficacy standards, thereby safeguarding public health. Notably, firms with sophisticated QMS encounter fewer recalls and reduced rejection rates, underscoring the financial advantages of efficient management of standards. In 2022, the regulatory and adherence management segment accounted for 18.7% of the pharmaceutical management systems market, underscoring the increasing focus on adherence within the industry.
As the market is projected to expand at a CAGR of 13.1% by 2032, understanding the QMS full form in pharma is paramount for managing regulatory challenges and enhancing standards. Furthermore, tools like Lumino provide AI-powered regulatory intelligence, enabling pharmaceutical teams to access accurate guidance and streamline document management, which is essential for maintaining compliance and operational efficiency.
Explain the Importance of QMS in Pharmaceutical Operations
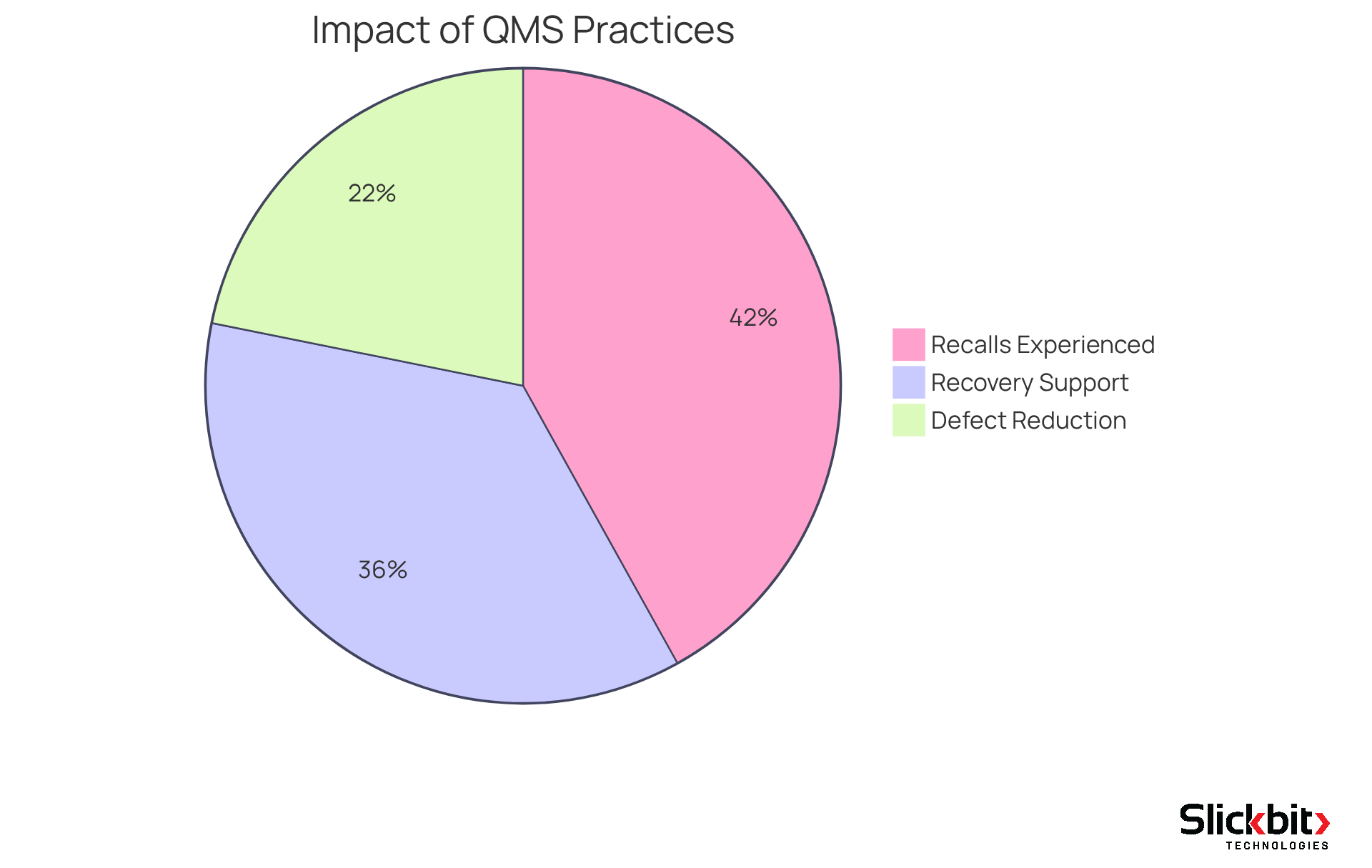
The significance of the QMS full form in pharma operations is paramount. It serves as the foundation for ensuring that products are consistently produced to meet stringent performance criteria. A well-executed QMS not only identifies and mitigates risks associated with product standards but also significantly reduces the likelihood of costly recalls and regulatory penalties. For instance, 96% of organizations have reported experiencing a recall of goods in the last five years, underscoring the critical need for effective management practices. Moreover, as Susan Fasso indicates, "A management system offers a framework for a company to guarantee that the standard of their medication adheres to regulations and ensures patient safety as its main function."
A QMS fosters a culture of continuous improvement, enabling companies to swiftly adapt to changing regulations and market demands. By implementing a robust QMS, pharmaceutical organizations can enhance operational efficiency, improve customer satisfaction, and ultimately achieve superior business outcomes. Real-world examples illustrate that organizations utilizing quality management solutions have seen a significant improvement in recovery from recalls, with 83% indicating that such systems supported their recovery efforts. Furthermore, manufacturers report reductions in defects by over 50% at optimal investment levels, further demonstrating the benefits of investing in a QMS. This highlights the essential role of the QMS full form in pharma in driving operational excellence within the pharmaceutical sector.
Identify Key Components of a Pharmaceutical QMS
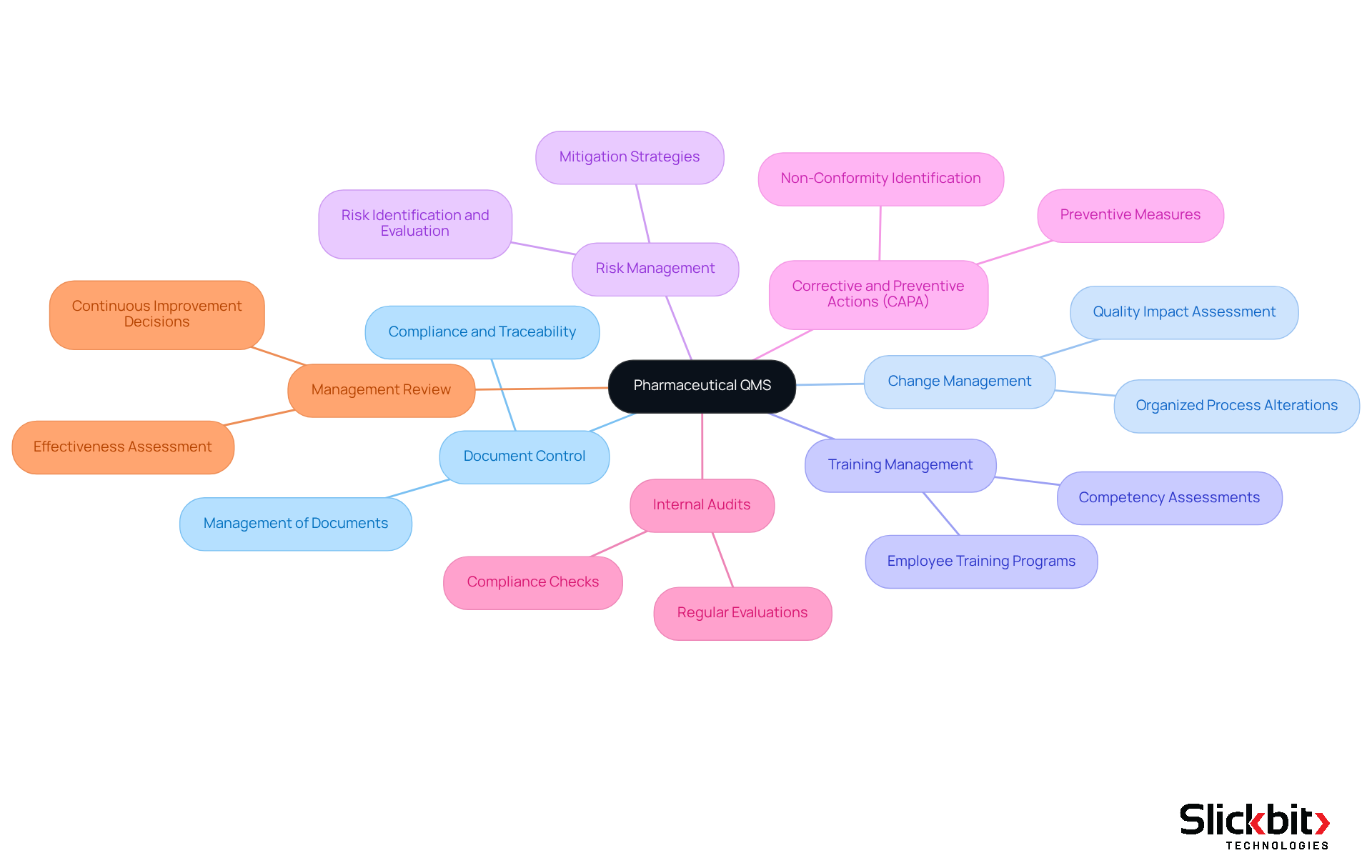
The qms full form in pharma refers to the key components of a Pharmaceutical Quality Management System, which are crucial for ensuring quality and compliance in pharmaceutical operations.
- Document Control: This component ensures that all documents are meticulously managed, reviewed, and approved, maintaining compliance and traceability.
- Change Management: It facilitates the organized management of alterations to processes, ensuring that adjustments do not adversely affect the quality of the output.
- Training Management: This guarantees that all staff are adequately trained and proficient in their roles, which is essential for upholding industry standards.
- Risk Management: It involves recognizing, evaluating, and mitigating risks that could impact product quality and adherence to regulations.
- Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA): A structured approach is applied to identify and address non-conformities while preventing their recurrence.
- Internal Audits: Regular evaluations of the QMS full form in pharma are conducted to ensure adherence to established procedures and identify areas for improvement.
- Management Review: Periodic evaluations by management assess the effectiveness of the QMS, enabling informed decisions for continuous improvement.
These components work in unison to create a comprehensive system that supports quality assurance and regulatory compliance in pharmaceutical operations.
Conclusion
Understanding the full form of QMS in the pharmaceutical sector is paramount for any organization aiming for excellence in product quality and regulatory compliance. This structured framework not only integrates diverse processes and policies but also acts as a cornerstone for upholding high standards within the pharmaceutical industry. By effectively managing risks and promoting continuous improvement, a robust QMS guarantees that products not only meet safety and efficacy standards but also contribute positively to public health.
The discussion underscores several critical aspects regarding the significance of a Quality Management System in pharmaceutical operations. It highlights the necessity of a well-executed QMS in minimizing recalls and regulatory penalties, ultimately protecting both the organization and consumers. Furthermore, the exploration of essential components—such as document control, change management, and risk management—illustrates how each element is vital in creating an effective QMS that bolsters compliance and operational efficiency.
In light of the increasing complexities within the pharmaceutical sector, investing in a comprehensive QMS is more crucial than ever. As the industry continues to evolve, organizations must prioritize the implementation of quality management systems to adeptly navigate regulatory challenges and enhance their operational capabilities. Embracing these practices not only leads to improved product quality but also positions companies for sustainable success in a competitive landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does QMS stand for in the pharmaceutical industry?
QMS stands for Quality Management System, which is a structured framework that integrates policies, processes, and procedures to ensure consistent standards of excellence and adherence to regulatory requirements.
What is the purpose of a QMS in pharma?
The purpose of a QMS in pharma is to enhance product quality and operational efficiency, effectively manage risks, maintain compliance, and foster continuous improvement within pharmaceutical companies.
How do AI technologies impact QMS in the pharmaceutical industry?
AI technologies, such as Slickbit.ai's Trend 483, help pharmaceutical companies identify trends in systemic risks and regulatory concerns derived from FDA 483s, thereby improving their QMS by informing risk management and regulatory strategies.
What are the benefits of implementing a robust QMS in pharmaceutical companies?
A robust QMS helps ensure that products meet safety and efficacy standards, reduces the likelihood of recalls and rejection rates, and offers financial advantages through efficient management of standards.
What percentage of the pharmaceutical management systems market was accounted for by regulatory and adherence management in 2022?
In 2022, the regulatory and adherence management segment accounted for 18.7% of the pharmaceutical management systems market.
What is the projected growth rate of the pharmaceutical management systems market by 2032?
The pharmaceutical management systems market is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.1% by 2032.
How do tools like Lumino contribute to QMS in the pharmaceutical industry?
Tools like Lumino provide AI-powered regulatory intelligence, enabling pharmaceutical teams to access accurate guidance and streamline document management, which is essential for maintaining compliance and operational efficiency.




