Overview
In quality management, CAPA stands for Corrective and Preventive Action, a crucial process for identifying and resolving issues that impact product quality and regulatory compliance. Its significance is underscored by a dual approach: addressing existing problems through corrective actions while simultaneously preventing future issues. This is particularly vital in industries such as pharmaceuticals, where strict adherence to regulations is paramount. By implementing CAPA effectively, organizations can not only rectify current deficiencies but also establish a proactive framework that safeguards against potential risks, ensuring sustained compliance and quality assurance.
Introduction
The landscape of quality management is increasingly defined by the systematic approach known as Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA). This critical framework not only addresses existing quality issues but also proactively seeks to eliminate potential problems before they arise, making it indispensable in industries where compliance is non-negotiable.
Furthermore, as organizations strive for operational excellence, the integration of advanced technologies, such as AI, introduces new dimensions to CAPA processes. However, as the demand for stringent regulatory adherence grows, companies must consider how to ensure that their CAPA systems are not only effective but also continuously improving.
Define CAPA: Full Form and Significance in Quality Management
The capa full form in quality refers to Corrective and Preventive Action, a systematic approach integral to quality management. It serves to identify, investigate, and resolve issues impacting product quality and compliance. The significance of this process is underscored by its dual focus: corrective actions address existing problems, while preventive measures aim to eliminate potential issues before they manifest. This proactive methodology is vital in sectors such as pharmaceuticals and biotechnology, where adherence to regulatory standards is essential for ensuring product safety and efficacy.
Furthermore, the integration of AI tools, such as Trend 483, can enhance the effectiveness of corrective and preventive action processes. By recognizing patterns in systemic risks and recurring violations from FDA inspections, Trend 483 empowers users to search, filter, and access complete 483s directly. This capability provides deeper insights into compliance and supports the optimization of management efforts.
Trace the Evolution of CAPA: Historical Context and Development
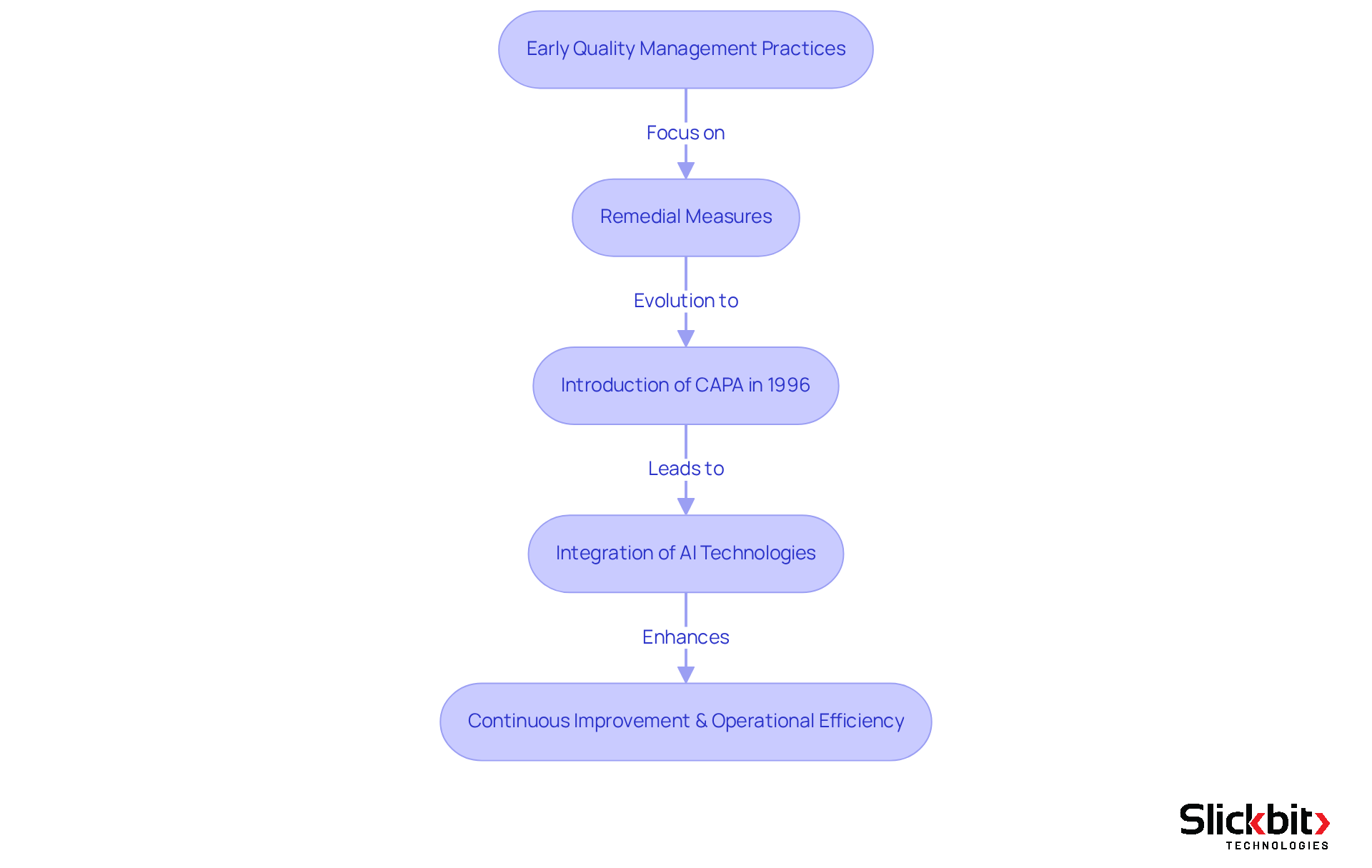
The concept of the capa full form in quality originates from the early quality management practices in the manufacturing sector. Initially, it focused primarily on remedial measures to address product flaws. However, with the evolution of industries and the establishment of stricter guidelines by regulatory bodies like the FDA, the necessity for preventive actions became increasingly evident.
The formal introduction of corrective and preventive actions in the 1996 FDA Quality System Regulation marked a pivotal moment, emphasizing the critical role of both corrective and preventive measures in understanding the capa full form in quality and ensuring product compliance.
Furthermore, the recent integration of AI technologies has transformed the landscape of corrective and preventive actions. Organizations can now leverage data from FDA inspections to identify systemic risks and recurring violations. The AI system empowers users to search, filter, and access comprehensive FDA 483s directly, providing deeper insights that enhance corrective and preventive actions.
This evolution not only highlights the imperative for continuous improvement but also emphasizes the need for operational efficiency in management systems, particularly within Life Sciences, where compliance is of utmost importance.
Examine Key Components of CAPA: Processes and Methodologies
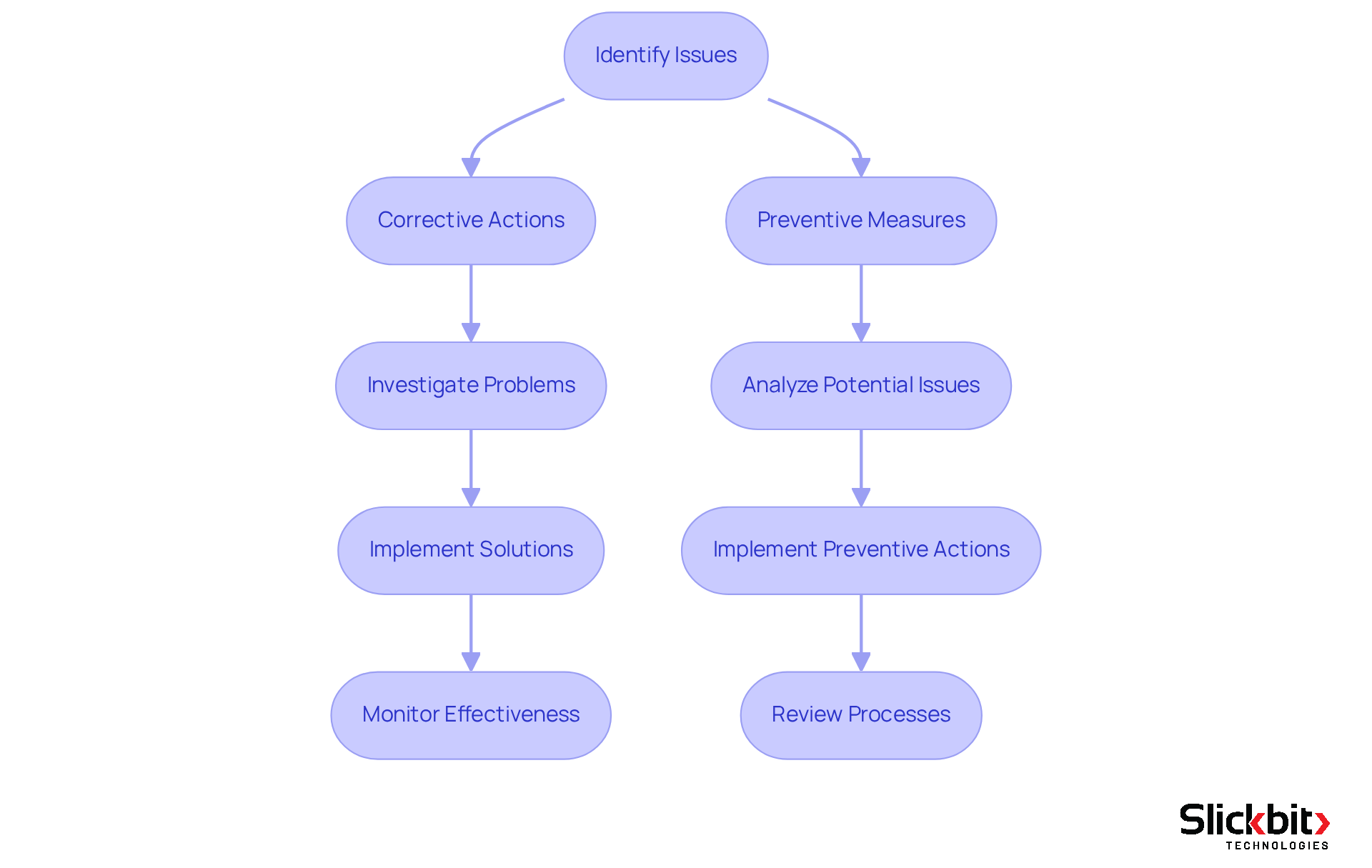
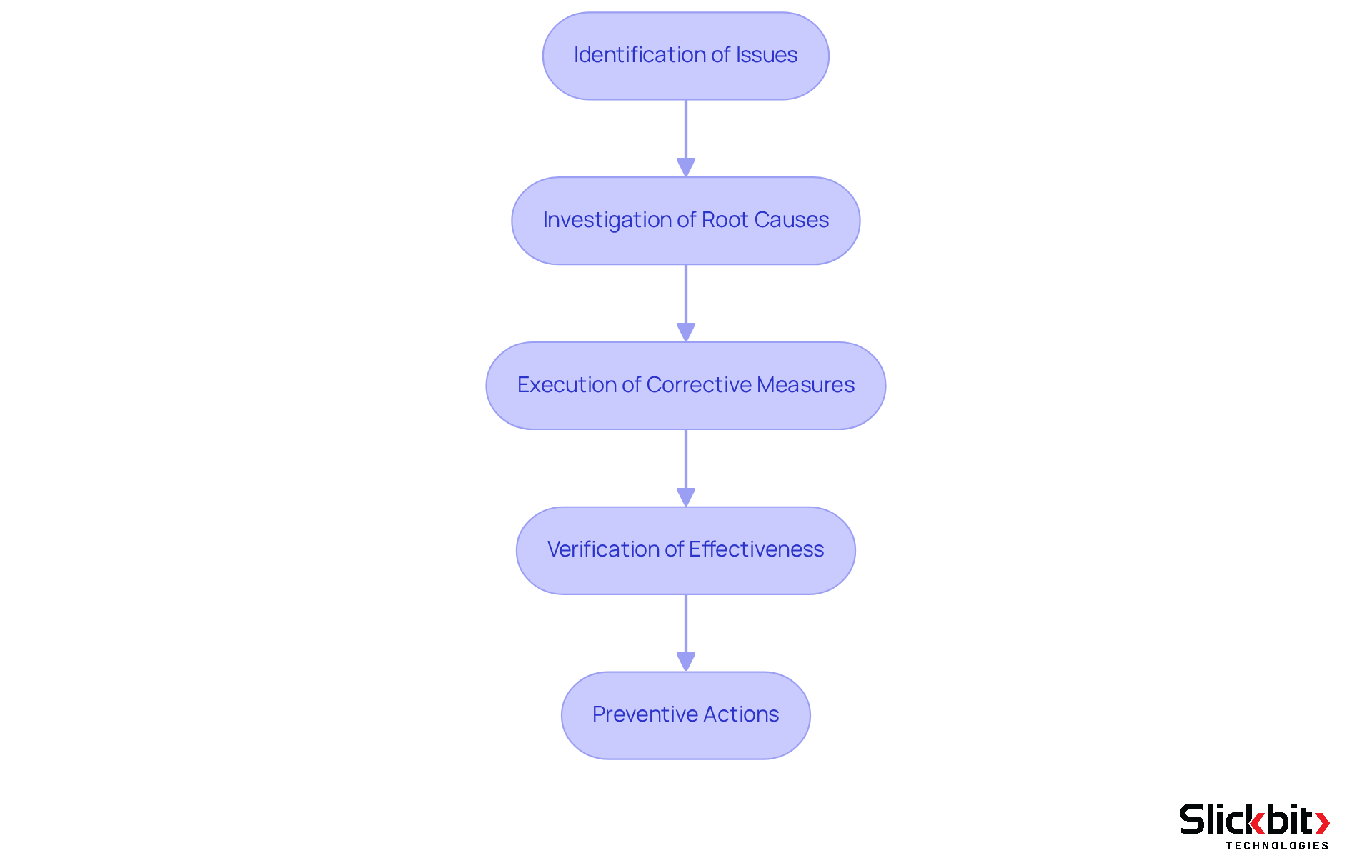
The essential elements of a CAPA system, also referred to by its capa full form in quality, encompass several critical steps:
- Identification of issues
- Investigation of root causes
- Execution of corrective measures
- Verification of effectiveness
This process typically commences with the detection of a non-conformance or quality issue, followed by a comprehensive investigation aimed at uncovering the underlying causes. Once the root cause is determined, corrective measures are implemented to address the immediate issue, alongside the development of preventive measures designed to minimize the likelihood of recurrence.
Verification entails a thorough assessment of the effectiveness of these actions, ensuring that the issues have been resolved and will not reoccur. This organized methodology is vital for maintaining compliance and enhancing overall management.
Furthermore, leveraging AI insights can significantly enhance these processes by identifying patterns in systemic risks and recurring infractions from FDA inspections, thereby informing more effective corrective and preventive action strategies.
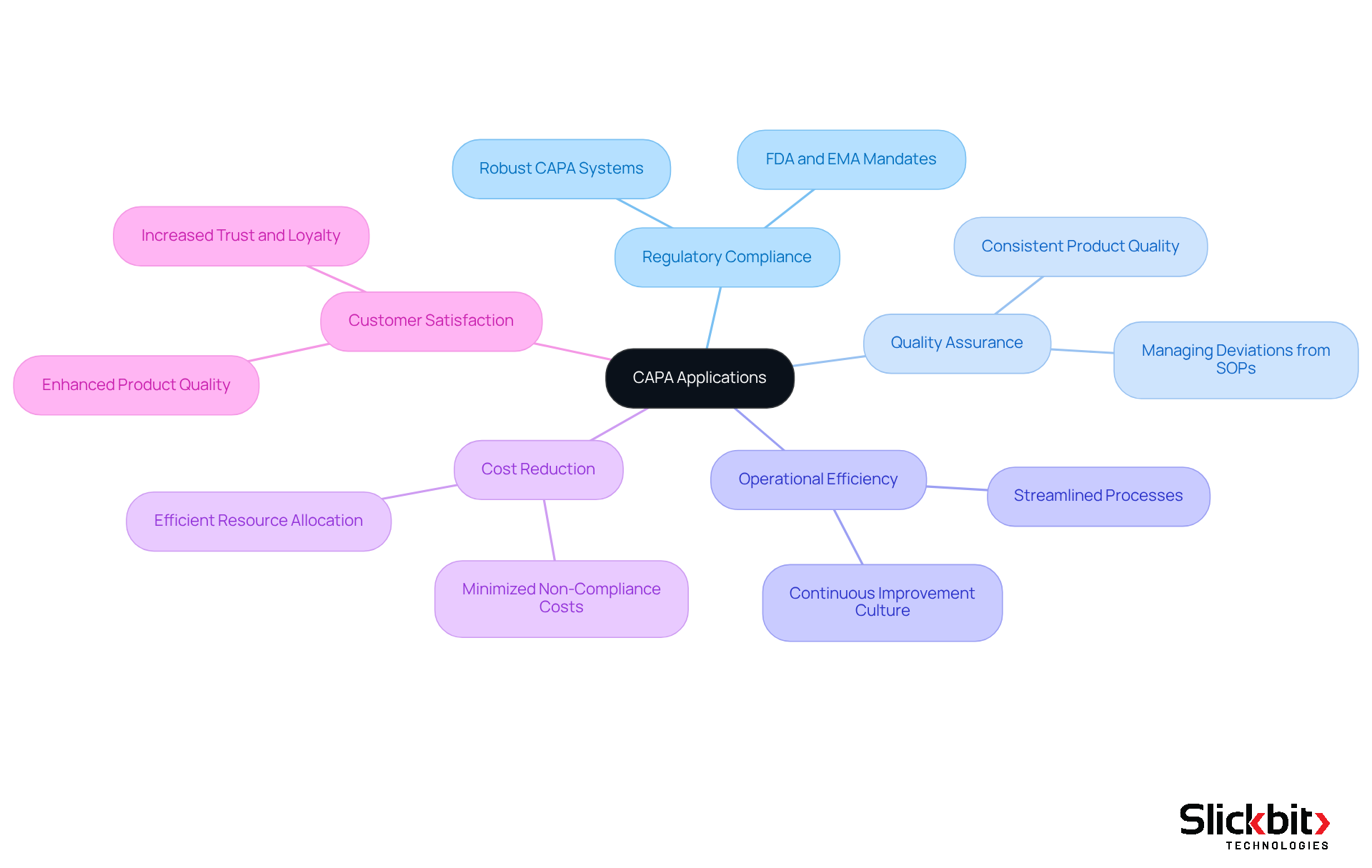
Explore CAPA Applications: Importance in Regulatory Compliance and Quality Assurance
The capa full form in quality, known as Corrective and Preventive Actions, is crucial for regulatory adherence and assurance across various sectors, particularly in Life Sciences. Regulatory bodies, such as the FDA and EMA, mandate that companies uphold robust CAPA systems, which include the capa full form in quality, to swiftly address and prevent issues related to compliance standards.
For example, in pharmaceutical production, CAPA processes are indispensable for managing deviations from standard operating procedures (SOPs), ensuring that products consistently meet safety and efficacy standards.
Furthermore, effective implementation of the CAPA full form in quality can enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs associated with non-compliance, and improve customer satisfaction by guaranteeing consistent product quality.
Companies must prioritize the establishment of strong CAPA systems to navigate regulatory landscapes effectively and foster a culture of continuous improvement.
Conclusion
Understanding the full form of CAPA—Corrective and Preventive Action—reveals its crucial role in quality management systems. This systematic approach not only addresses existing quality issues but also proactively prevents potential problems, making it indispensable in sectors where compliance and product safety are paramount. Furthermore, the integration of advanced technologies, such as AI, enhances the effectiveness of CAPA processes, ensuring that organizations can navigate the complexities of regulatory requirements with greater efficiency.
Throughout this article, key components of the CAPA process have been outlined, including:
- The identification of issues
- Investigation of root causes
- Execution of corrective measures
- Verification of effectiveness
Each step is vital for maintaining compliance and improving overall management practices. The historical evolution of CAPA, particularly its formal recognition by regulatory bodies, underscores the increasing importance of both corrective and preventive actions in ensuring product quality and compliance.
Ultimately, the significance of CAPA extends beyond mere compliance; it fosters a culture of continuous improvement and operational efficiency. Organizations must prioritize the development and implementation of robust CAPA systems to not only meet regulatory standards but also enhance customer satisfaction and product integrity. Embracing the principles of CAPA is essential for any company committed to excellence in quality management.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does CAPA stand for in quality management?
CAPA stands for Corrective and Preventive Action.
What is the purpose of CAPA in quality management?
The purpose of CAPA is to identify, investigate, and resolve issues that impact product quality and compliance.
How does CAPA differentiate between corrective and preventive actions?
Corrective actions address existing problems, while preventive measures aim to eliminate potential issues before they occur.
Why is CAPA important in certain sectors?
CAPA is vital in sectors such as pharmaceuticals and biotechnology because adherence to regulatory standards is essential for ensuring product safety and efficacy.
How can AI tools enhance the CAPA process?
AI tools, like Trend 483, can enhance the CAPA process by recognizing patterns in systemic risks and recurring violations from FDA inspections, providing deeper insights into compliance and optimizing management efforts.




