Overview
The FDA-approved drug approval process represents a complex, multi-step journey designed to ensure that new medications are both safe and effective. This intricate pathway commences with drug discovery and culminates in the submission of a New Drug Application (NDA) for market authorization.
Critical phases of this process include:
- Preclinical studies
- Clinical trials
These phases are essential for validating the efficacy and safety of new drugs. Furthermore, the importance of regulatory compliance and cross-functional team coordination cannot be overstated; these elements are vital for navigating the myriad challenges that arise during the approval process. By enhancing collaboration among diverse teams, the likelihood of successful approvals is significantly increased.
Introduction
Navigating the intricate landscape of the FDA drug approval process is essential for achieving pharmaceutical success. This process encompasses a rigorous series of evaluations designed to ensure both safety and effectiveness. The multi-step journey involves extensive research and clinical trials, requiring a profound understanding of regulatory compliance and the latest technological advancements. With high stakes and significant challenges at every phase, organizations must consider how to streamline their approach effectively. Enhancing the likelihood of approval is not just a goal; it is a necessity in today’s competitive pharmaceutical landscape.
Explore the Fundamentals of the FDA Drug Approval Process
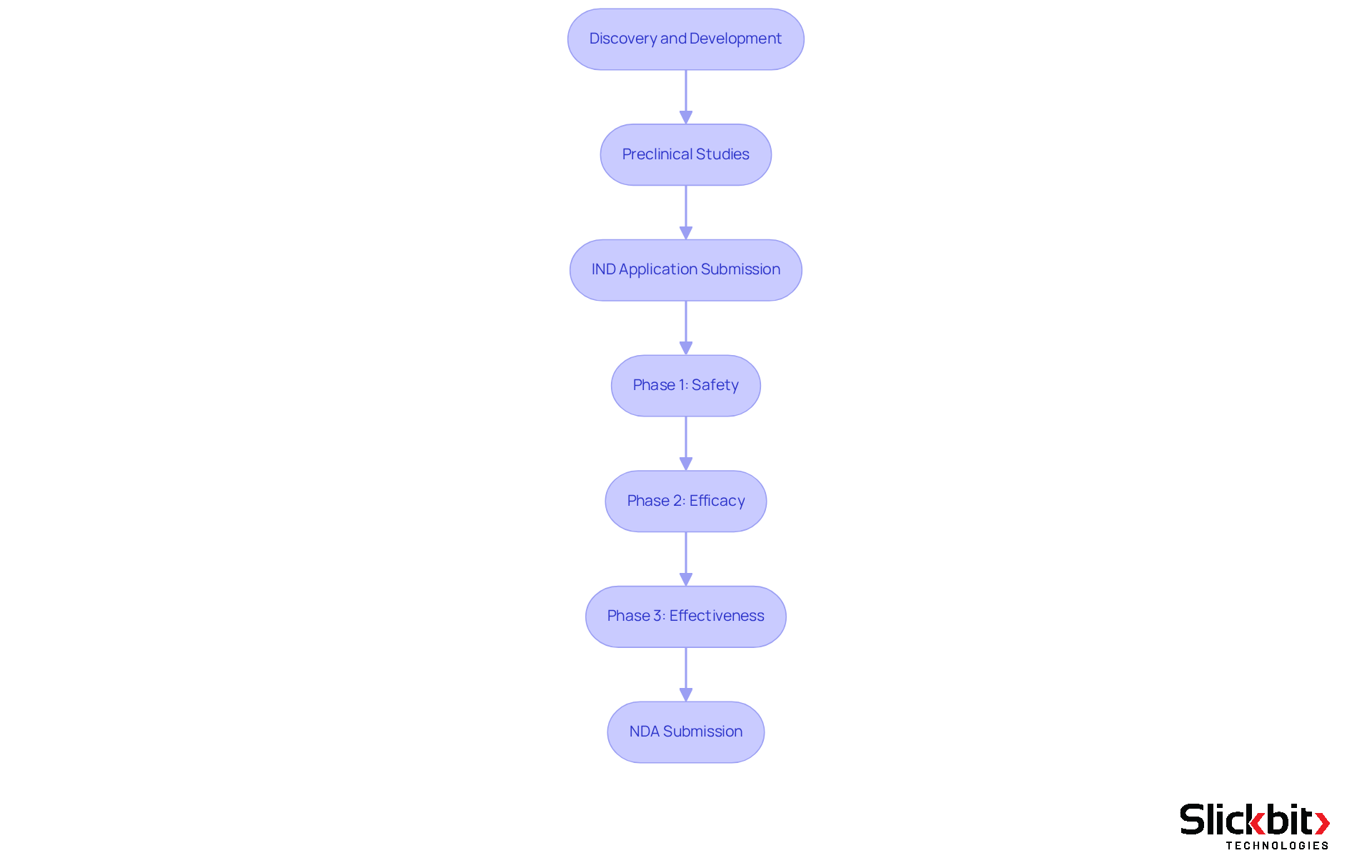
The FDA approval process for medications represents a comprehensive, multi-step journey meticulously designed to ensure that new substances are both safe and effective for public use. It commences with the discovery and development stage, where researchers diligently identify potential treatment candidates. Following this initial phase, preclinical studies rigorously evaluate the medication's safety and biological activity within laboratory settings.
Once sufficient information is amassed, the sponsor submits an Investigational New Product (IND) application to the FDA, which must receive approval before clinical trials can commence. The clinical phase is systematically divided into three stages:
- Phase 1 concentrates on safety
- Phase 2 assesses efficacy
- Phase 3 confirms effectiveness across a larger population
Notably, around 50%-60% of substances entering Phase 3 trials ultimately secure FDA authorization, underscoring the critical importance of this phase. Upon successful trials, the process culminates in the New Drug Application (NDA) submission, where comprehensive data from clinical trials is meticulously assessed by the FDA to ascertain if the medication can be marketed.
Importantly, approximately 85%-90% of NDAs submitted to the FDA receive approval, although regulatory delays can occasionally arise. Recent modifications within the FDA's medication approval system—including the integration of artificial intelligence tools to streamline evaluations—are transforming the assessment of applications. Understanding these fundamentals is essential for navigating the complexities of pharmaceutical development and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
Detail the Phases of Drug Development Leading to FDA Approval
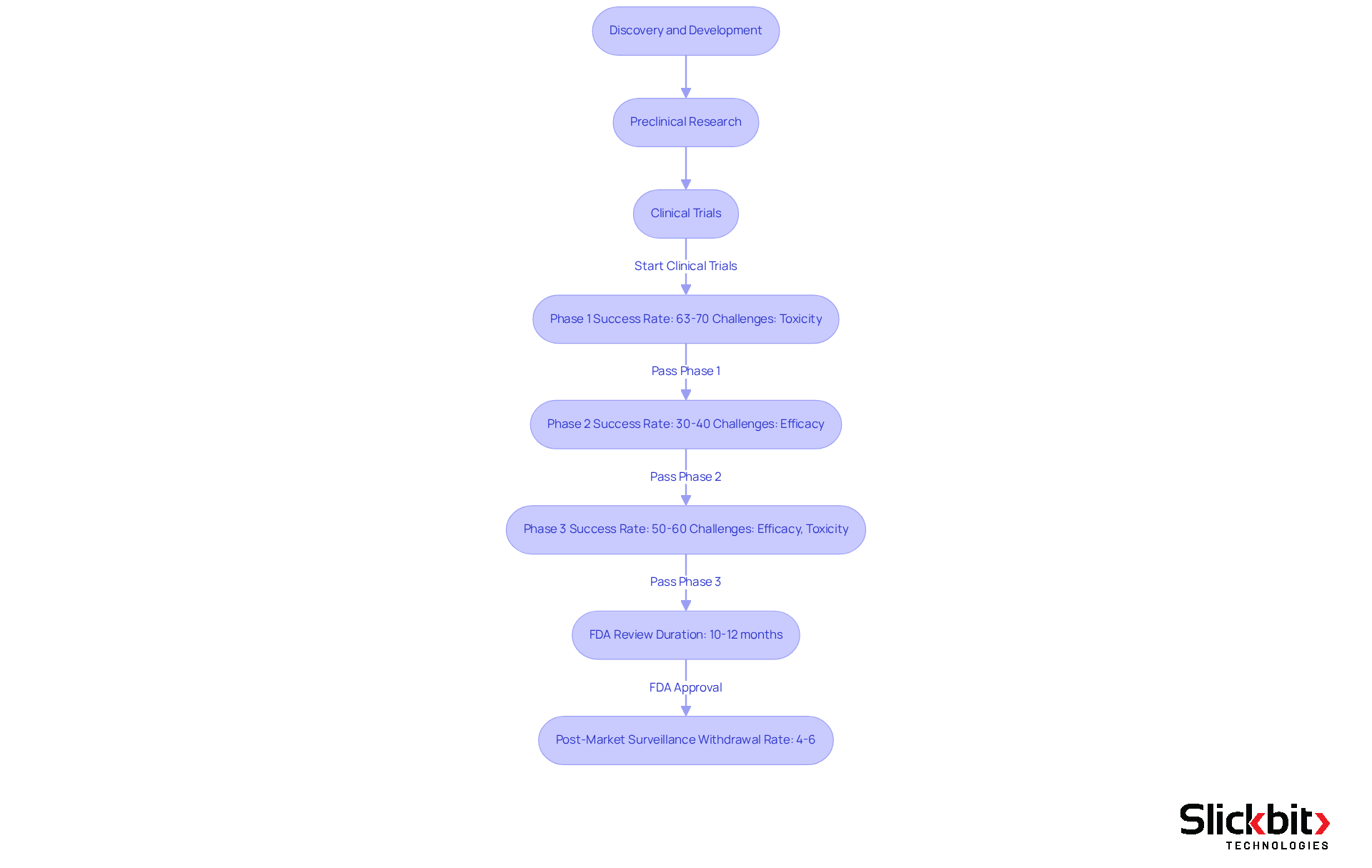
The pharmaceutical development process is a multifaceted journey that encompasses several critical phases. Discovery and Development marks the initial stage where researchers identify and synthesize new compounds. Following this, Preclinical Research involves laboratory and animal studies aimed at assessing safety and biological activity. The process then transitions into Clinical Trials, which are divided into three essential parts:
- Phase 1 focuses on safety and dosage, typically involving 20 to 100 healthy volunteers. Approximately 63%-70% of medications successfully pass this phase, although nearly a third fail due to toxicity concerns.
- Phase 2 assesses the treatment's efficacy and side effects in a larger patient group, with only about 30%-40% of substances advancing to Phase 3. This phase is crucial for demonstrating meaningful clinical benefits. Notably, the typical probability of initial approval among prominent pharmaceutical firms is approximately 14.3%, highlighting the challenges faced in medication development.
- Phase 3 entails comprehensive testing across diverse populations to verify effectiveness and observe adverse reactions, with approximately 50%-60% of oncology treatments failing at this stage due to inadequate efficacy or unforeseen toxicity.
Subsequently, the FDA Review process commences. After successful trials, a New Drug Application (NDA) is submitted for FDA approval, which typically spans 10-12 months under standard review before the drug can be considered FDA approved. Finally, Post-Market Surveillance ensures that once authorized, the medication is monitored for long-term effects and safety within the general population. Approximately 4%-6% of approved substances are withdrawn from the market due to safety concerns. Each stage is vital for confirming that the medication meets rigorous safety and efficacy standards prior to market entry, underscoring the significance of thorough clinical trials in medication evaluation.
Navigate Regulatory Compliance and Challenges in Drug Approval
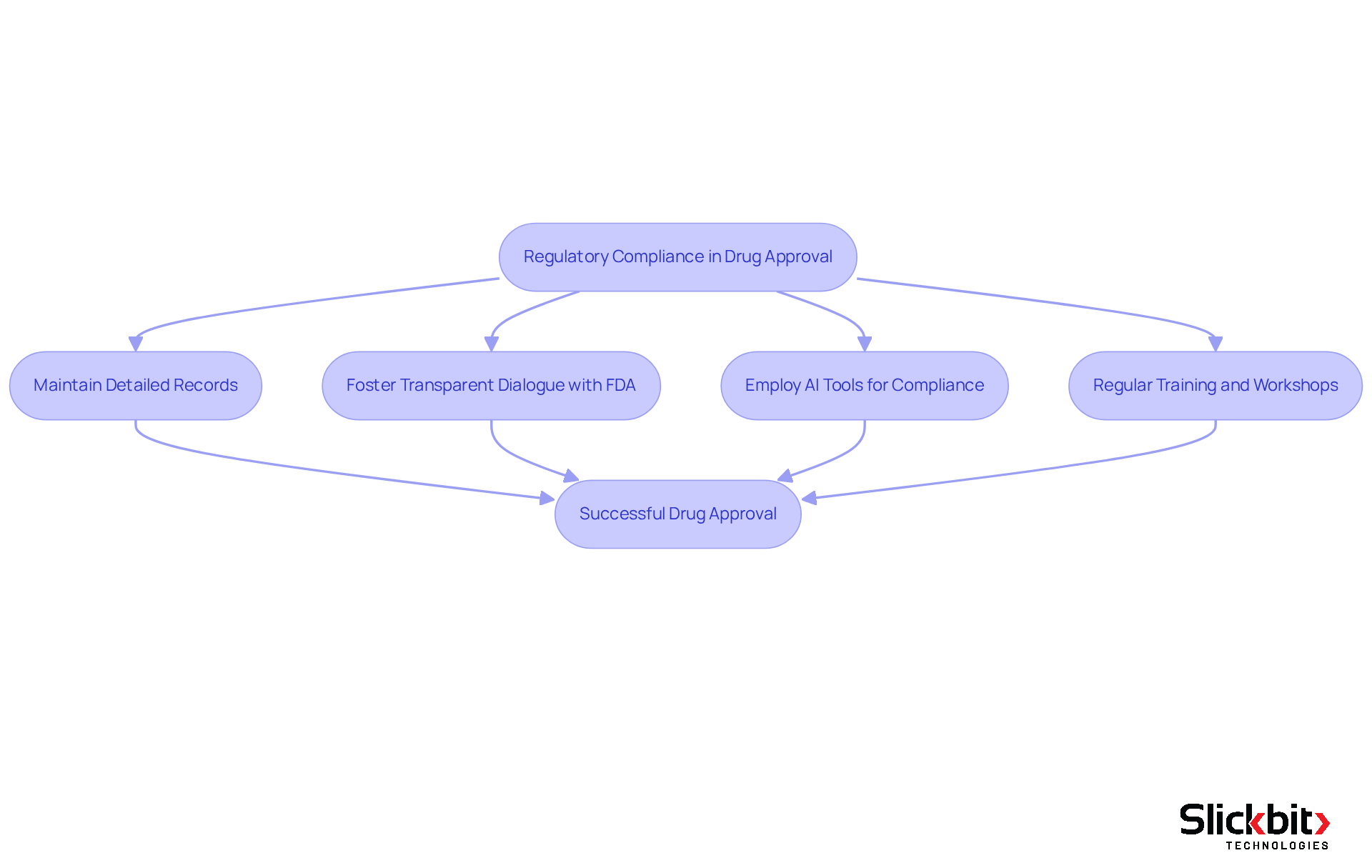
Regulatory compliance in drug authorization is critical, necessitating strict adherence to the guidelines that are FDA approved. Companies often encounter challenges, such as inadequate clinical data, which can lead to application delays or denials. To effectively navigate these obstacles, it is essential to maintain detailed records and foster transparent dialogue with the FDA during the evaluation phase.
AI-driven tools are increasingly employed to enhance data management and compliance tracking, significantly mitigating the risk of errors. For instance, GlaxoSmithKline implemented an AI-powered compliance system that notably reduced documentation errors during internal audits, thereby minimizing the risk of regulatory citations. Furthermore, predictive AI models can anticipate regulators' questions, resulting in faster response times and fewer follow-up inquiries.
Understanding the FDA's evolving guidelines is paramount, as the agency is now receptive to submissions that are FDA approved and utilize 'AI-enhanced' features to improve efficiency while upholding safety standards. Organizations that proactively address potential compliance challenges can streamline their FDA approved processes. Regular training and workshops for teams involved in medication development not only foster a culture of compliance but also enhance awareness of regulatory requirements. This proactive approach is vital, particularly as the FDA emphasizes the necessity for transparency and accountability in AI applications, ensuring that human oversight remains integral to the regulatory process.
Enhance Cross-Functional Team Coordination for Successful Approvals
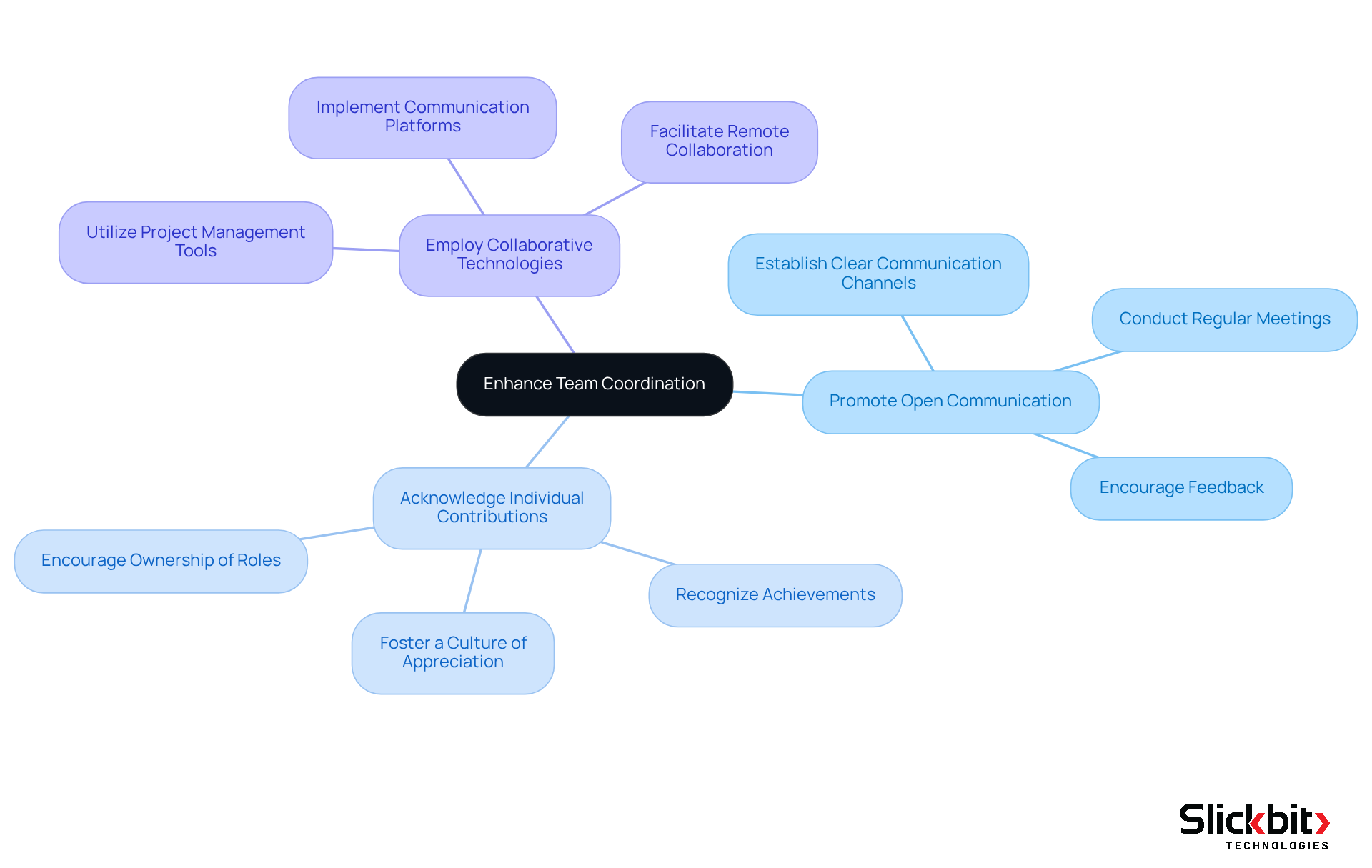
Effective cross-functional team coordination is essential in pharmaceutical product development, requiring the integration of expertise from R&D, regulatory affairs, and marketing. Establishing clear communication channels and conducting regular meetings align goals and expectations, fostering a collaborative environment. Furthermore, utilizing project management tools significantly impacts approval timelines by facilitating collaboration and keeping all team members informed about progress and challenges. For instance, Roche, a leader in R&D expenditure, exemplifies how organized project management can optimize workflows and enhance productivity.
Cultivating an environment of collaboration and collective accountability enhances problem-solving capabilities, leading to more effective development processes. Involving all relevant stakeholders early in the process, particularly before regulatory interactions, aids in identifying potential issues and streamlining the path to obtaining consent. As industry leaders assert, effective collaboration transcends mere teamwork; it involves leveraging each member's strengths to achieve common objectives. As specialists note, 'the strength of the team is each individual member, and the strength of each member is the team,' underscoring the importance of collaborative effort in navigating the complexities of drug authorization.
Best practices for enhancing team collaboration in pharmaceutical R&D include:
- Promoting open communication
- Acknowledging individual contributions
- Employing collaborative technologies
By implementing these strategies, teams can significantly boost their efficiency and effectiveness, ultimately leading to FDA approved drug approvals.
Conclusion
Mastering the FDA drug approval process is essential for pharmaceutical success, ensuring that new medications undergo rigorous evaluation for safety and efficacy before reaching the public. This intricate journey, spanning from initial discovery to post-market surveillance, highlights the importance of each phase in validating a drug's potential benefits and risks. A comprehensive understanding of this process not only aids in compliance but also significantly enhances the likelihood of successful approvals.
Key insights from the article illuminate the structured phases of drug development, including:
- Discovery
- Preclinical research
- Clinical trials
Each phase presents its own challenges and success rates. The importance of regulatory compliance is paramount, as navigating potential obstacles is crucial for timely approvals. Furthermore, the role of cross-functional team coordination emerges as a vital factor in ensuring that all aspects of drug development are harmonized, ultimately leading to more efficient and effective processes.
As the pharmaceutical landscape continues to evolve, embracing innovative strategies and technologies will be pivotal. Organizations must prioritize collaboration, transparency, and adaptability in their approaches to drug development. By fostering a culture of teamwork and leveraging advanced tools for compliance and communication, companies can significantly enhance their chances of successfully navigating the FDA approval process, thereby contributing to the delivery of safe and effective medications to those in need.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the FDA drug approval process?
The FDA drug approval process is a comprehensive, multi-step journey designed to ensure that new medications are safe and effective for public use.
What are the initial stages of the drug approval process?
The process begins with the discovery and development stage, where researchers identify potential treatment candidates, followed by preclinical studies that evaluate the medication's safety and biological activity in laboratory settings.
What is an Investigational New Product (IND) application?
An IND application is submitted by the sponsor to the FDA for approval before clinical trials can begin, containing information about the drug's safety and proposed clinical study plans.
How is the clinical phase of drug approval structured?
The clinical phase is divided into three stages: Phase 1 focuses on safety, Phase 2 assesses efficacy, and Phase 3 confirms effectiveness across a larger population.
What is the success rate of substances entering Phase 3 trials?
Approximately 50%-60% of substances that enter Phase 3 trials ultimately secure FDA authorization.
What happens after successful clinical trials?
After successful trials, the process culminates in the submission of a New Drug Application (NDA), where the FDA assesses comprehensive data from clinical trials to determine if the medication can be marketed.
What is the approval rate for NDAs submitted to the FDA?
Approximately 85%-90% of NDAs submitted to the FDA receive approval, although there can be regulatory delays.
How is the FDA's drug approval process evolving?
Recent modifications, including the integration of artificial intelligence tools, are streamlining the evaluation of applications and transforming the assessment process.


