Overview
The article highlights the critical steps that R&D managers must undertake to master regulatory Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls (CMC) for ensuring compliance and facilitating successful drug development. It underscores the necessity of comprehending regulatory CMC processes, fostering effective cross-functional collaboration, and implementing best practices. These strategies are pivotal as they significantly increase the probability of timely drug approvals and mitigate compliance risks linked to manufacturing and quality deficiencies.
Introduction
Regulatory Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls (CMC) stands as a pivotal component in the pharmaceutical landscape, ensuring drug products consistently meet rigorous quality standards throughout their lifecycle.
For R&D managers, mastering CMC processes is essential; it not only mitigates compliance risks but also significantly increases the likelihood of successful drug approvals and timely market entry.
However, a staggering percentage of Investigational New Drug submissions encounter delays due to CMC-related issues. This raises a critical question: how can R&D leaders effectively navigate the complexities of regulatory compliance to foster innovation while adhering to evolving standards?
The answer lies in a strategic approach that balances compliance with innovative practices.
Define CMC and Its Importance in Regulatory Affairs
Regulatory CMC encompasses the fundamental processes and documentation vital for ensuring that pharmaceutical products are consistently produced and controlled in alignment with rigorous quality standards. Regulatory CMC serves as a cornerstone of compliance affairs, ensuring the identity, strength, quality, and purity of drug products throughout their development lifecycle. For R&D managers, a comprehensive understanding of regulatory CMC is crucial for navigating the complexities of compliance submissions and ensuring adherence to guidelines set forth by authorities such as the FDA and EMA. This expertise not only mitigates risks associated with product quality and non-compliance but also significantly enhances the likelihood of successful drug approvals and timely market entry.
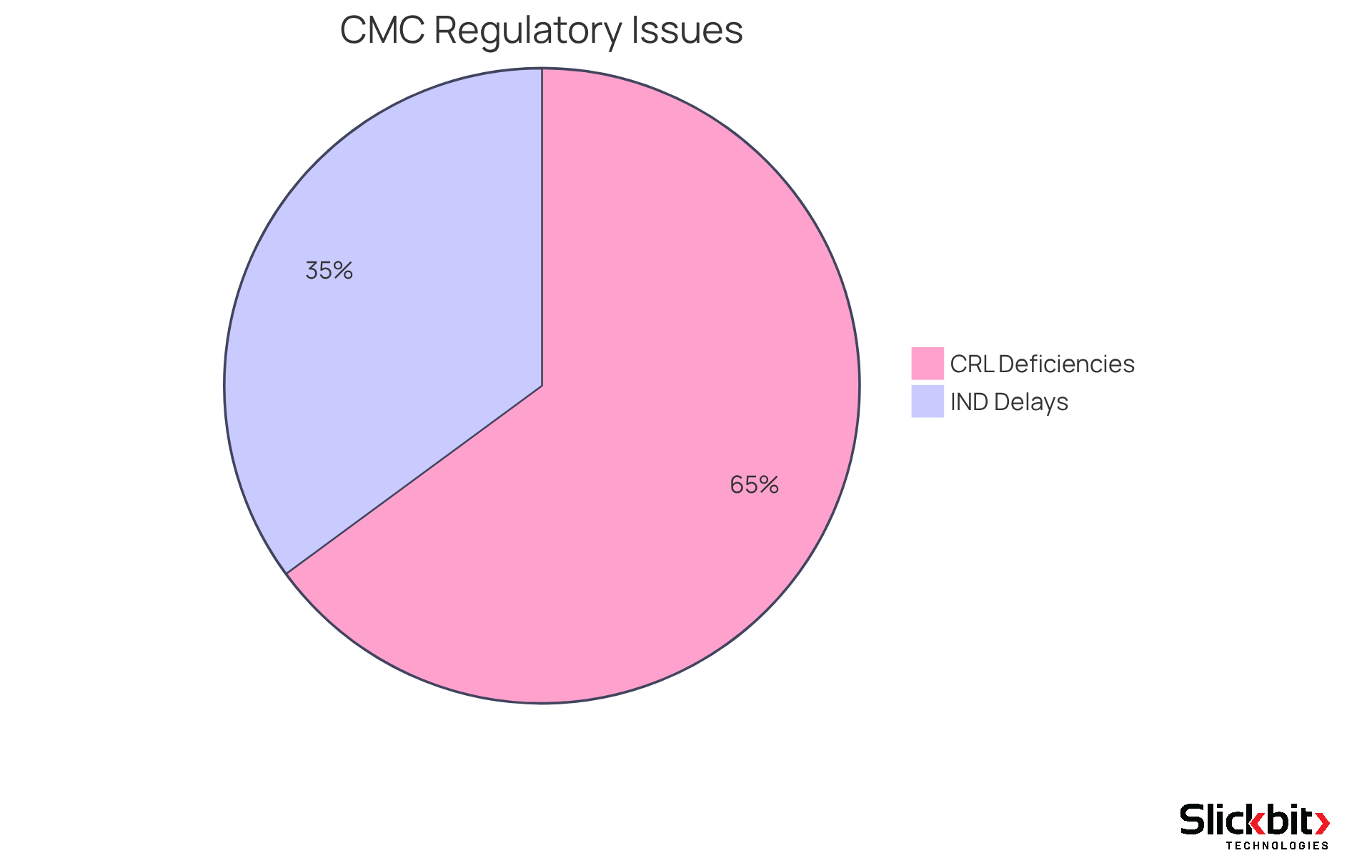
Recent trends reveal that approximately 40% of Investigational New Drug (IND) submissions encounter delays due to regulatory CMC issues, underscoring the imperative for robust CMC practices. Furthermore, with 74% of Complete Response Letters (CRLs) issued from 2020 to 2024 citing manufacturing or quality deficiencies, the significance of regulatory CMC in maintaining high standards cannot be overstated. By prioritizing regulatory CMC compliance, pharmaceutical firms can streamline their development processes and enhance their chances of approval success.
The FDA's heightened oversight emphasizes that scientific innovation is merely one facet of the challenge in advanced therapy development. It becomes essential for R&D leaders to integrate regulatory CMC considerations early in the process and foster cross-functional collaboration to meet evolving compliance expectations.
Identify the Role of R&D Managers in CMC Compliance
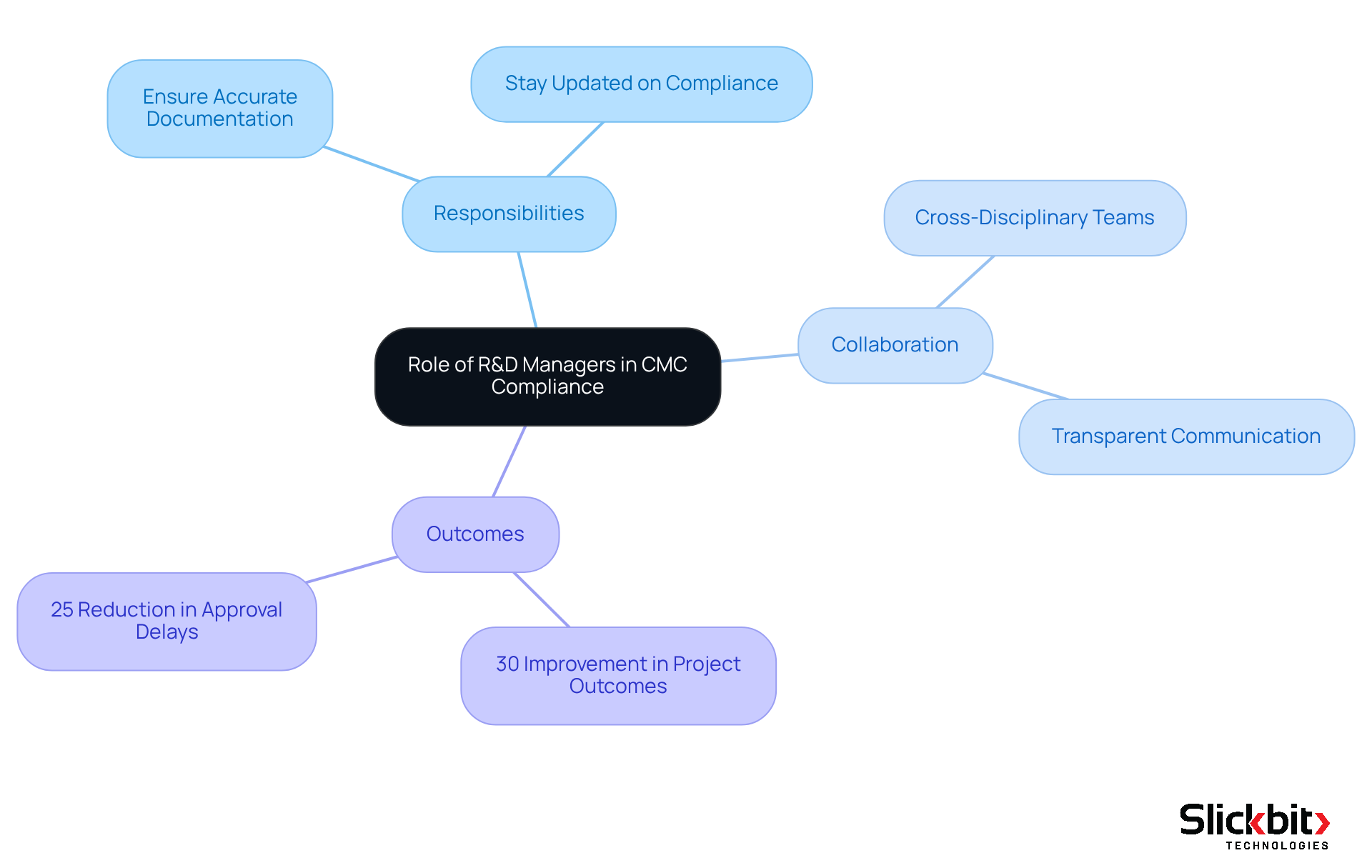
R&D managers play a pivotal role in developing and executing Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls (CMC) strategies within their organizations. Their primary responsibility is to ensure that all CMC documentation is not only accurate and complete but also adheres to stringent compliance standards. This involves collaborating with cross-disciplinary groups, including quality assurance, manufacturing, and compliance affairs, to ensure that CMC practices align with broader organizational objectives.
In 2025, effective collaboration among these teams is more crucial than ever. Studies indicate that cross-functional teamwork can enhance project outcomes by up to 30%. R&D supervisors must remain vigilant and knowledgeable about evolving compliance guidelines and industry best practices to navigate the complexities of CMC adherence skillfully. By fostering a culture of teamwork and transparent communication, R&D leaders can significantly enhance the effectiveness of CMC processes, thus reducing the likelihood of compliance setbacks.
Successful execution of CMC strategies frequently relies on the proactive engagement of R&D leaders. For instance, organizations that have adopted a structured approach to CMC documentation have reported a 25% reduction in approval delays. By prioritizing these responsibilities, R&D leaders not only contribute to the successful development of pharmaceutical products but also enhance their organizations' capacity to meet compliance expectations and market demands.
Implement Best Practices for CMC Authoring
To implement best practices for CMC authoring, R&D managers must focus on several key strategies that ensure compliance and enhance documentation quality.
-
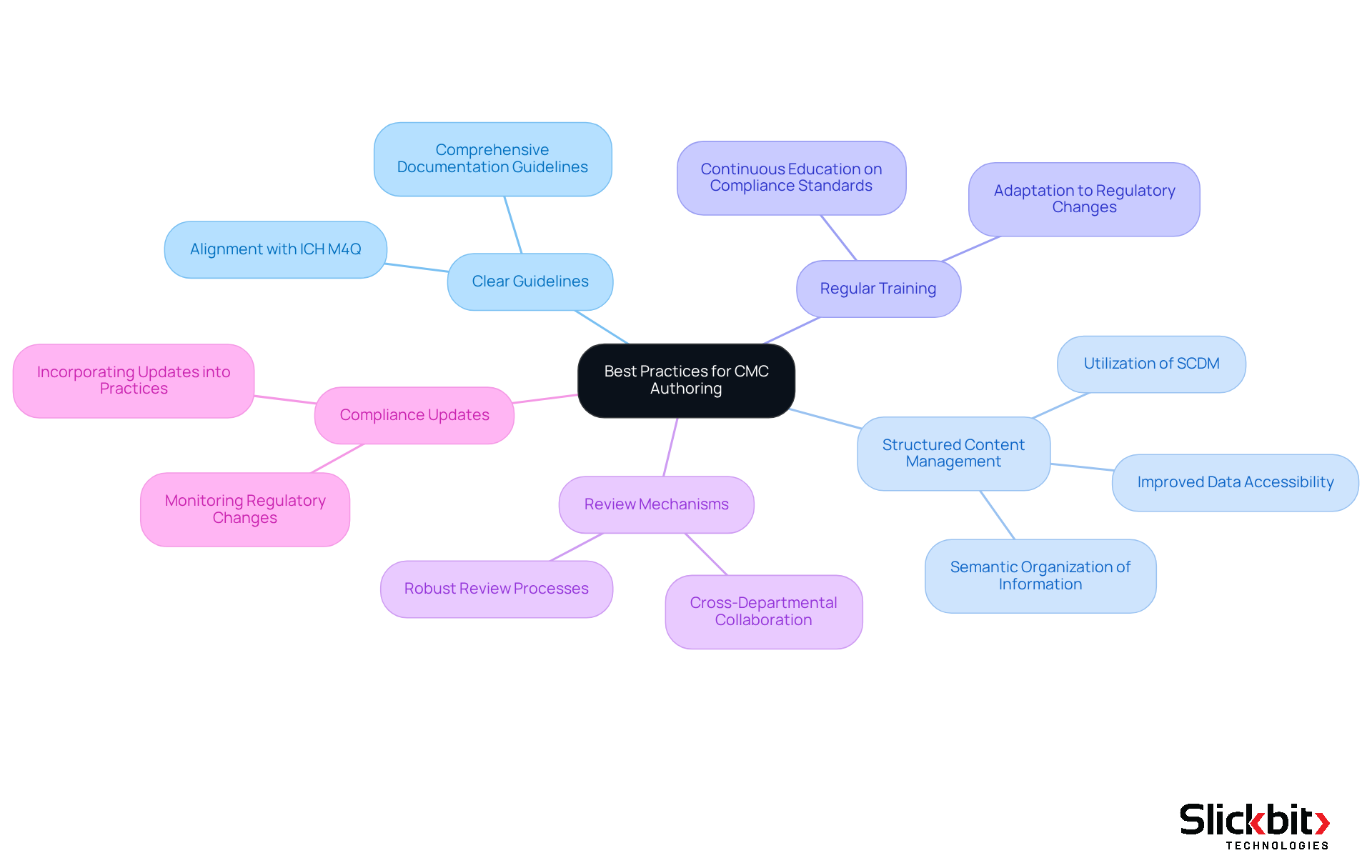
Establish Clear Guidelines: It is essential to develop comprehensive guidelines for CMC documentation that outline the required content, format, and review processes. This guarantees consistency and clarity across all submissions, aligning with compliance expectations such as ICH M4Q.
-
Utilize Structured Content Management: Leveraging structured content management systems (SCDM) is crucial for organizing and managing CMC documents efficiently. SCDM improves data accessibility and collaboration, enabling teams to create semantically organized blocks of information that are both human and machine-readable. This approach not only enhances submission quality but also outlines the end-to-end scientific data lifecycle, facilitating better compliance and efficiency.
-
Conduct Regular Training: Continuous education for individuals involved in CMC authoring is vital to ensure they are well-acquainted with compliance standards and best practices. This commitment to training upholds high documentation quality standards and equips teams to adapt to changing regulatory environments.
-
Implement Review and Feedback Mechanisms: Establishing a robust review process that incorporates input from various departments is essential. This collaborative approach helps identify potential issues early, leveraging insights from scientific and statistical teams to enhance the overall quality of CMC submissions.
-
Stay Informed on Compliance Changes: Regularly monitoring updates to compliance guidelines and incorporating them into regulatory CMC authoring practices is a proactive strategy that helps minimize the risk of non-compliance. This vigilance enhances the credibility of submissions, ensuring that documentation meets the stringent requirements of regulatory bodies like the FDA, EMA, and PMDA.
Overcome Common Challenges in CMC Navigation
Navigating regulatory cmc presents several challenges for R&D leaders, each requiring strategic approaches to ensure success. Here are common obstacles and strategies to overcome them:
-
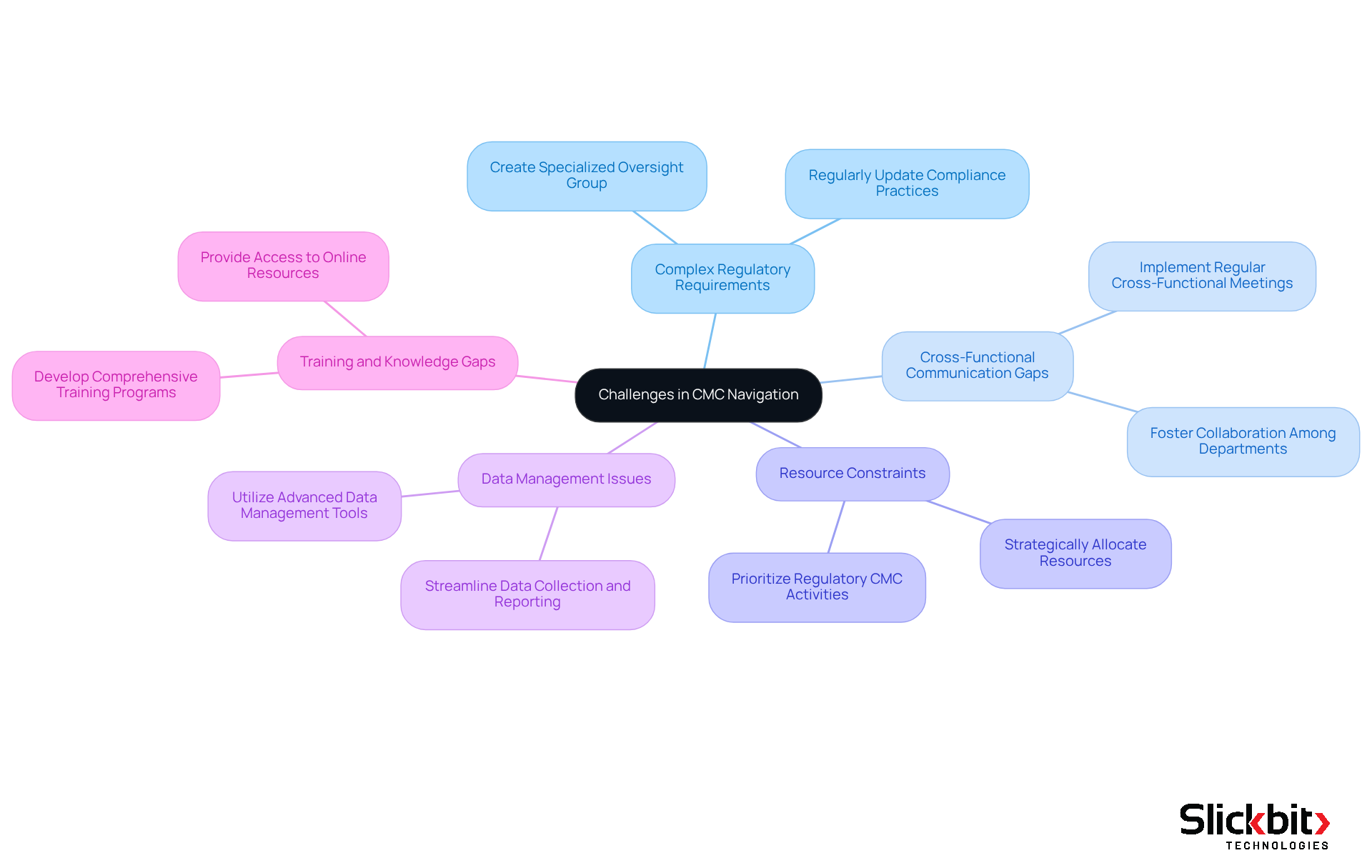
Complex Regulatory Requirements: Regulatory guidelines are intricate and frequently updated, with over 230 new or revised guidelines issued since 2020. To mitigate compliance risks, R&D supervisors should create a specialized group dedicated to overseeing these changes. This ensures that all practices related to regulatory CMC conform to current requirements, significantly reducing the risk of compliance failures.
-
Cross-Functional Communication Gaps: Effective communication among departments is crucial for CMC success. Implementing regular cross-functional meetings fosters collaboration and ensures that all stakeholders are aligned on regulatory CMC objectives. This approach addresses the common issue of siloed information, which can lead to compliance oversights.
-
Resource Constraints: Limited resources can hinder CMC efforts, with an average-sized hospital spending nearly $7.6 million annually on compliance activities. R&D managers must prioritize regulatory CMC activities and allocate resources strategically. This ensures that critical tasks are completed on time, thereby optimizing operational efficiency.
-
Data Management Issues: Managing large volumes of data can be overwhelming. Notably, 43% of companies have discovered unauthorized Excel spreadsheets performing critical calculations. To combat this, utilizing advanced data management tools can streamline data collection, analysis, and reporting processes. This guarantees that all documentation related to regulatory CMC is accurate and up-to-date.
-
Training and Knowledge Gaps: Ongoing training is vital for keeping group members informed about best practices in regulatory cmc. Developing a comprehensive training program that includes workshops, seminars, and access to online resources enhances the team's knowledge and skills in CMC compliance. This approach addresses the looming expertise gap, particularly as 40% of experienced quality professionals are expected to retire by 2030.
Conclusion
Mastering regulatory Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls (CMC) stands as a crucial pursuit for R&D managers who seek to adeptly navigate the intricate landscape of pharmaceutical development and compliance. A comprehensive understanding of CMC processes not only mitigates potential risks but also significantly enhances the likelihood of successful drug approvals and timely market entry. By placing a strong emphasis on CMC compliance, R&D leaders can optimize their operations and play a pivotal role in the overall success of their organizations.
Key responsibilities of R&D managers include:
- Establishing clear documentation guidelines
- Fostering cross-functional collaboration
- Implementing best practices for CMC authoring
Staying informed about evolving regulatory requirements is paramount, and effective communication alongside resource management emerges as critical in overcoming the common challenges encountered in CMC navigation. By adopting structured approaches and engaging in continuous training, R&D managers can markedly improve compliance outcomes.
Ultimately, mastery of regulatory CMC transcends mere compliance; it represents a strategic advantage in the competitive realm of drug development. R&D managers are urged to embrace these best practices and cultivate a culture of compliance within their teams. This proactive approach not only enhances their organizations' capabilities but also reduces the risk of delays, thereby contributing to the advancement of innovative therapies that benefit patients across the globe.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does CMC stand for in regulatory affairs?
CMC stands for Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls, which encompasses the processes and documentation necessary for ensuring pharmaceutical products are produced and controlled according to quality standards.
Why is regulatory CMC important?
Regulatory CMC is crucial for ensuring the identity, strength, quality, and purity of drug products throughout their development lifecycle, thus serving as a cornerstone of compliance affairs.
How does understanding regulatory CMC benefit R&D managers?
A comprehensive understanding of regulatory CMC helps R&D managers navigate compliance submissions and adhere to guidelines set by authorities like the FDA and EMA, reducing risks associated with product quality and non-compliance.
What are the consequences of inadequate regulatory CMC practices?
Inadequate regulatory CMC practices can lead to delays in Investigational New Drug (IND) submissions, with approximately 40% of submissions experiencing such delays. Additionally, 74% of Complete Response Letters (CRLs) issued from 2020 to 2024 cited manufacturing or quality deficiencies.
How can pharmaceutical firms improve their chances of drug approval?
By prioritizing regulatory CMC compliance, pharmaceutical firms can streamline their development processes, thereby enhancing their chances of successful drug approvals and timely market entry.
What role does the FDA play in regulatory CMC?
The FDA emphasizes heightened oversight in regulatory CMC, indicating that scientific innovation alone is not sufficient for advanced therapy development. It is essential for R&D leaders to integrate regulatory CMC considerations early in the development process.
What is the significance of cross-functional collaboration in regulatory CMC?
Cross-functional collaboration is vital for meeting evolving compliance expectations and ensuring that regulatory CMC considerations are integrated throughout the product development process.




