Overview
The article underscores the critical need for R&D managers to master Current Good Manufacturing Practices (CGMP), as these regulations are essential for ensuring the safety, efficacy, and quality of pharmaceutical products. A comprehensive understanding and proactive management of CGMP deviations not only enhance product quality but also significantly reduce drug approval times and improve patient safety. Consequently, this demonstrates the strategic advantage of compliance within the pharmaceutical development process. By adhering to CGMP, organizations can position themselves favorably in a competitive market, ultimately leading to better health outcomes for patients.
Introduction
Current Good Manufacturing Practice (CGMP) is the cornerstone of pharmaceutical quality assurance, guaranteeing that products are consistently produced and controlled according to rigorous standards. For R&D managers, mastering CGMP deviations is not merely a regulatory obligation; it is a crucial pathway to enhancing product quality, safeguarding public health, and streamlining development processes.
However, a significant challenge persists: how can organizations effectively identify and rectify these deviations to avert costly repercussions and ensure compliance?
This article explores essential insights and strategies that empower R&D leaders to navigate the complexities of CGMP, ultimately transforming potential pitfalls into opportunities for innovation and excellence.
Define Current Good Manufacturing Practice (CGMP)
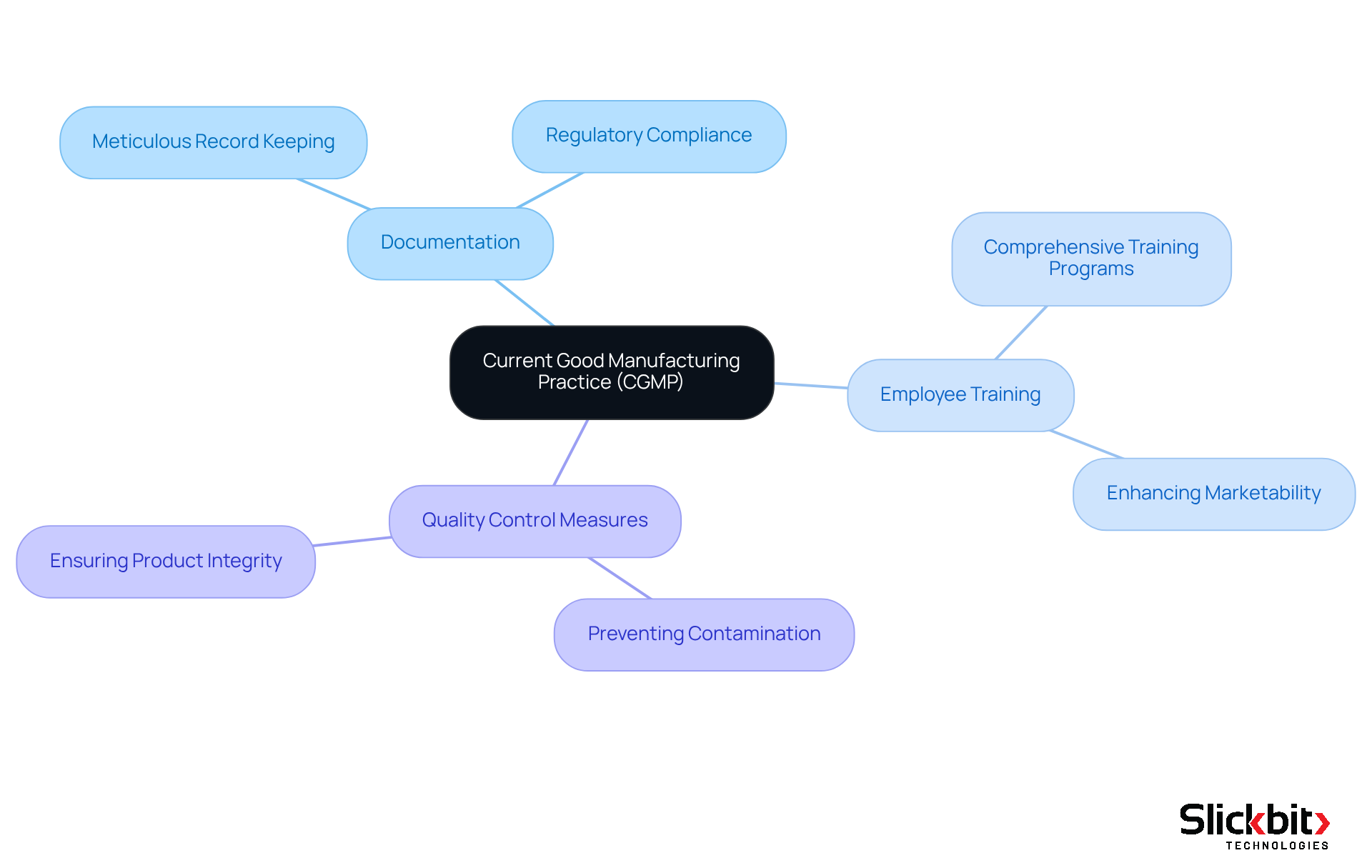
Current Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) embodies the FDA-imposed regulations that guarantee the consistent creation and regulation of pharmaceutical products according to stringent standards. These regulations encompass every aspect of production, from sourcing raw materials to maintaining the facilities and equipment used in manufacturing.
Manufacturers are required to establish robust management systems to ensure that products meet critical safety and efficacy standards. Key components of good manufacturing practices include:
- Meticulous documentation
- Comprehensive employee training
- Rigorous quality control measures designed to prevent contamination and production errors
Adhering to current good manufacturing practices is crucial not only for maintaining product integrity but also for safeguarding public health, as it helps prevent the distribution of unsafe or ineffective medications.
In 2025, statistics indicate that a significant majority of companies reviewed by the FDA are found to be in compliance with good manufacturing practices, underscoring the importance of these standards in the pharmaceutical industry. Notable examples of successful compliance with good manufacturing practices demonstrate how organizations can adeptly navigate regulatory challenges, thereby enhancing their operational efficiency and market credibility.
Explain the Importance of CGMP in Pharmaceutical Development
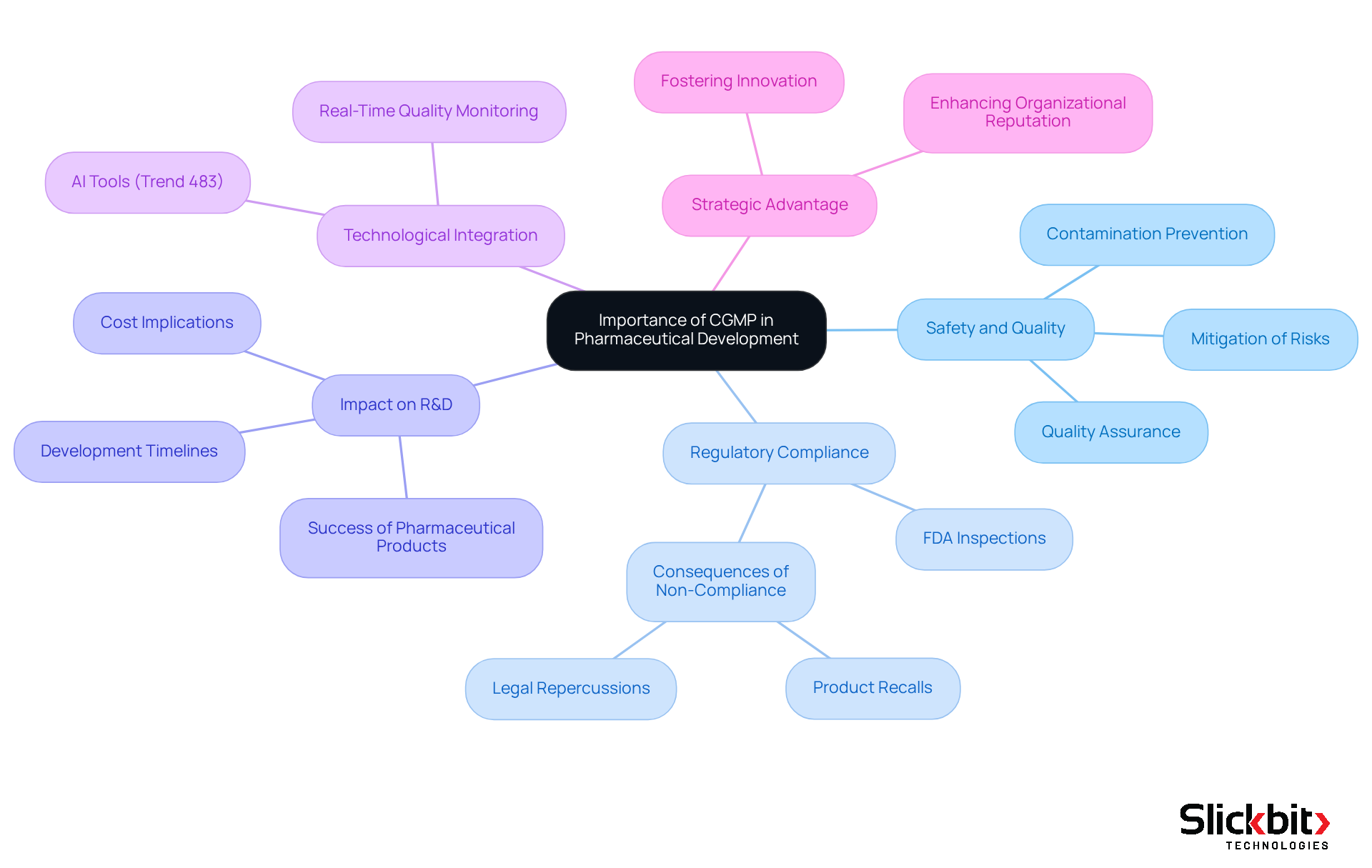
The significance of Current Good Manufacturing Practices (CGMP) and addressing CGMP deviations in pharmaceutical development cannot be overstated. These standards are established to ensure that products are safe, effective, and of the highest quality. By adhering to these practices, organizations significantly mitigate the risks of contamination, mix-ups, and errors, which can have severe health implications for patients. Moreover, compliance with CGMP deviations is essential for regulatory authorization; failing to meet these standards can result in serious consequences, such as product recalls and legal repercussions.
For R&D managers, a thorough understanding of CGMP is vital, as it directly influences development timelines, costs, and the overall success of pharmaceutical products. Integrating good manufacturing practices into the development process helps to address CGMP deviations, enhancing organizational reputation while ensuring patient safety and simplifying regulatory compliance. In 2025, companies that effectively implemented CGMP reported a notable decrease in drug approval times, underscoring the tangible benefits of adherence.
Additionally, adherence to regulations concerning CGMP deviations has been linked to improved patient safety metrics, with experts asserting that strict compliance can significantly diminish risks associated with drug production. The integration of AI tools, such as Trend 483, can further bolster adherence efforts by identifying trends in systemic risks and recurrent violations from FDA inspections. This technology empowers R&D managers to search, filter, and analyze FDA 483 reports for deeper insights, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency.
In conclusion, embedding CGMP within the pharmaceutical development framework transcends mere regulatory compliance; it serves as a strategic advantage that fosters innovation while safeguarding public health.
Identify and Address CGMP Deviations
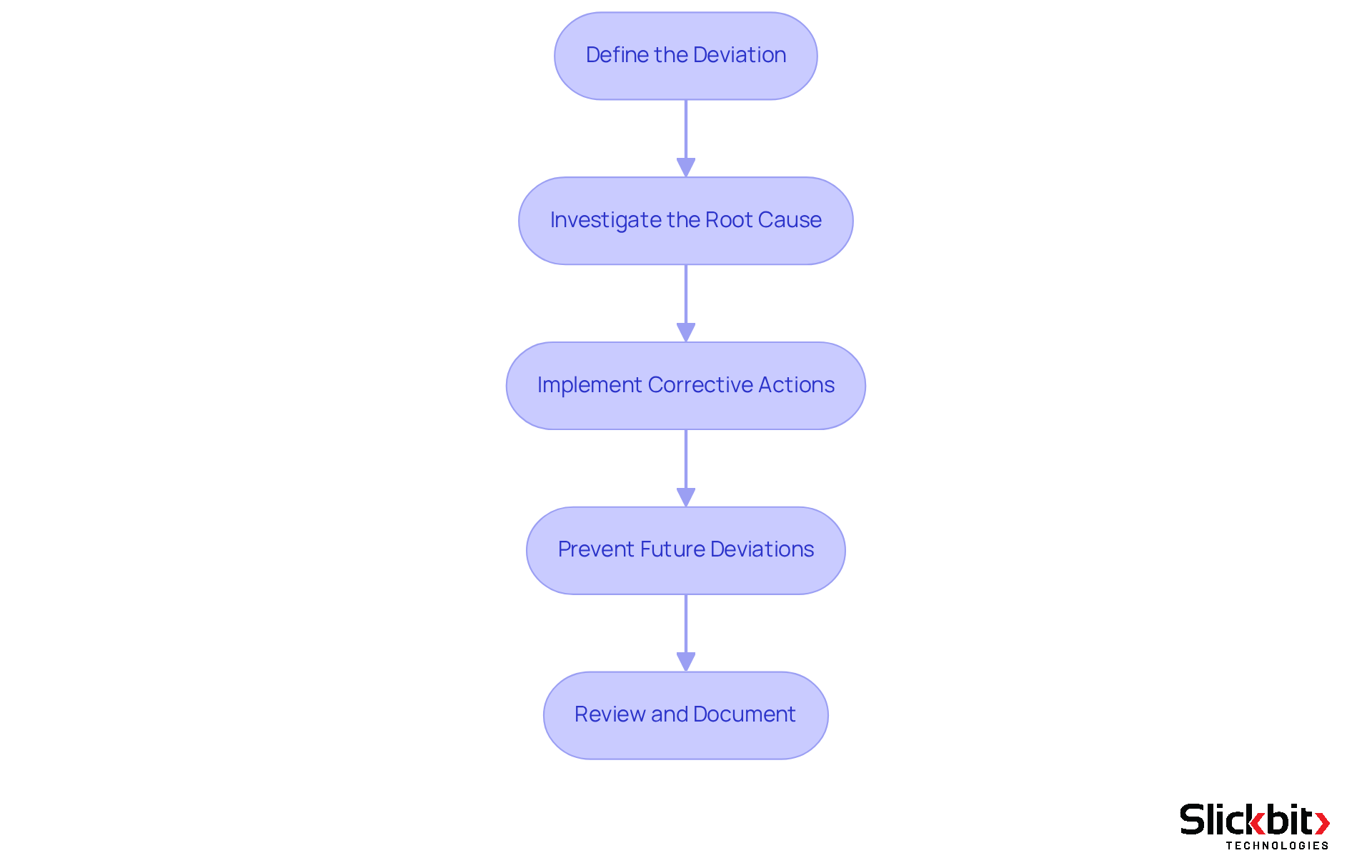
Recognizing and addressing cgmp deviations necessitates a systematic approach to ensure compliance and maintain the quality of the output. Deviations can manifest at any point in the manufacturing process, from the handling of raw materials to the testing of final products. To effectively manage these deviations, R&D managers should adhere to the following steps:
- Define the Deviation: Clearly document the nature of the deviation, specifying the procedures or standards that were not adhered to.
- Investigate the Root Cause: Conduct a comprehensive investigation to uncover the underlying cause of the deviation. This may involve reviewing documentation, interviewing staff, and analyzing processes.
- Implement Corrective Actions: Formulate and execute corrective actions to address the immediate cause of the deviation. This could involve retraining staff, revising procedures, or enhancing quality control measures.
- Prevent Future Deviations: Establish preventive measures to avert recurrence. This may include revising standard operating procedures (SOPs), enhancing training programs, or utilizing AI solutions such as Slickbit's Trend 483 tool for real-time monitoring and insights into systemic risks and adherence trends.
- Review and Document: Ensure that all findings, actions taken, and preventive measures are meticulously documented. This documentation is vital for regulatory compliance and future audits.
By proactively identifying and addressing cgmp deviations, R&D managers can enhance product quality, ensure regulatory compliance, and ultimately safeguard patient safety.
Conclusion
Mastering Current Good Manufacturing Practices (CGMP) is not merely beneficial; it is essential for ensuring the safety, efficacy, and quality of pharmaceutical products. This framework serves a dual purpose: it enables organizations to meet regulatory standards while simultaneously enhancing operational efficiency and bolstering their market reputation. By comprehensively understanding and implementing CGMP, R&D managers can adeptly navigate the complexities of drug development, all while prioritizing patient safety and compliance.
Throughout this article, we have provided key insights into the significance of CGMP in pharmaceutical development, particularly in mitigating risks associated with contamination and production errors. A structured approach to identifying and addressing CGMP deviations has been outlined, emphasizing the necessity of thorough documentation, root cause analysis, and the implementation of corrective actions. Furthermore, leveraging technology, such as AI tools, can significantly streamline compliance efforts, leading to improved outcomes in drug approval timelines and patient safety metrics.
Viewing the commitment to CGMP as a strategic advantage fosters innovation while simultaneously protecting public health. As the pharmaceutical landscape continues to evolve, embracing these practices transcends regulatory requirements; it becomes a vital component for success. Consequently, organizations are encouraged to prioritize CGMP adherence, ensuring that safety and quality remain at the forefront of their development processes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Current Good Manufacturing Practice (CGMP)?
Current Good Manufacturing Practice (CGMP) refers to the FDA-imposed regulations that ensure the consistent creation and regulation of pharmaceutical products according to strict standards.
What aspects of production do CGMP regulations cover?
CGMP regulations cover every aspect of production, including sourcing raw materials, maintaining facilities, and using equipment in manufacturing.
What are the key components of good manufacturing practices?
Key components of good manufacturing practices include meticulous documentation, comprehensive employee training, and rigorous quality control measures designed to prevent contamination and production errors.
Why is adherence to CGMP important?
Adhering to CGMP is crucial for maintaining product integrity and safeguarding public health, as it helps prevent the distribution of unsafe or ineffective medications.
What do statistics indicate about CGMP compliance in the pharmaceutical industry?
In 2025, statistics indicate that a significant majority of companies reviewed by the FDA were found to be in compliance with good manufacturing practices, highlighting the importance of these standards in the pharmaceutical industry.
How can successful compliance with CGMP impact organizations?
Successful compliance with CGMP can help organizations navigate regulatory challenges, enhance their operational efficiency, and improve their market credibility.




