Overview
This article delivers a comprehensive, step-by-step guide for developing effective Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA) within organizations, particularly in the life sciences sector. It underscores the critical need for identifying problems and investigating their root causes. By implementing corrective measures and continuously monitoring their effectiveness, organizations can significantly enhance quality and compliance. Furthermore, the article provides essential tools and resources designed to streamline the CAPA process, ensuring that organizations can effectively manage and mitigate issues as they arise.
Introduction
In the intricate realm of life sciences, effectively managing corrective and preventive actions (CAPA) is crucial for ensuring quality and compliance. Organizations encounter the dual challenge of resolving current issues while also proactively mitigating future risks. This article presents a detailed step-by-step guide for formulating a robust CAPA plan, showcasing essential strategies and tools designed to bolster operational integrity.
What are the pivotal elements that can determine the success or failure of a CAPA initiative, and how can organizations guarantee that their corrective actions foster enduring improvements?
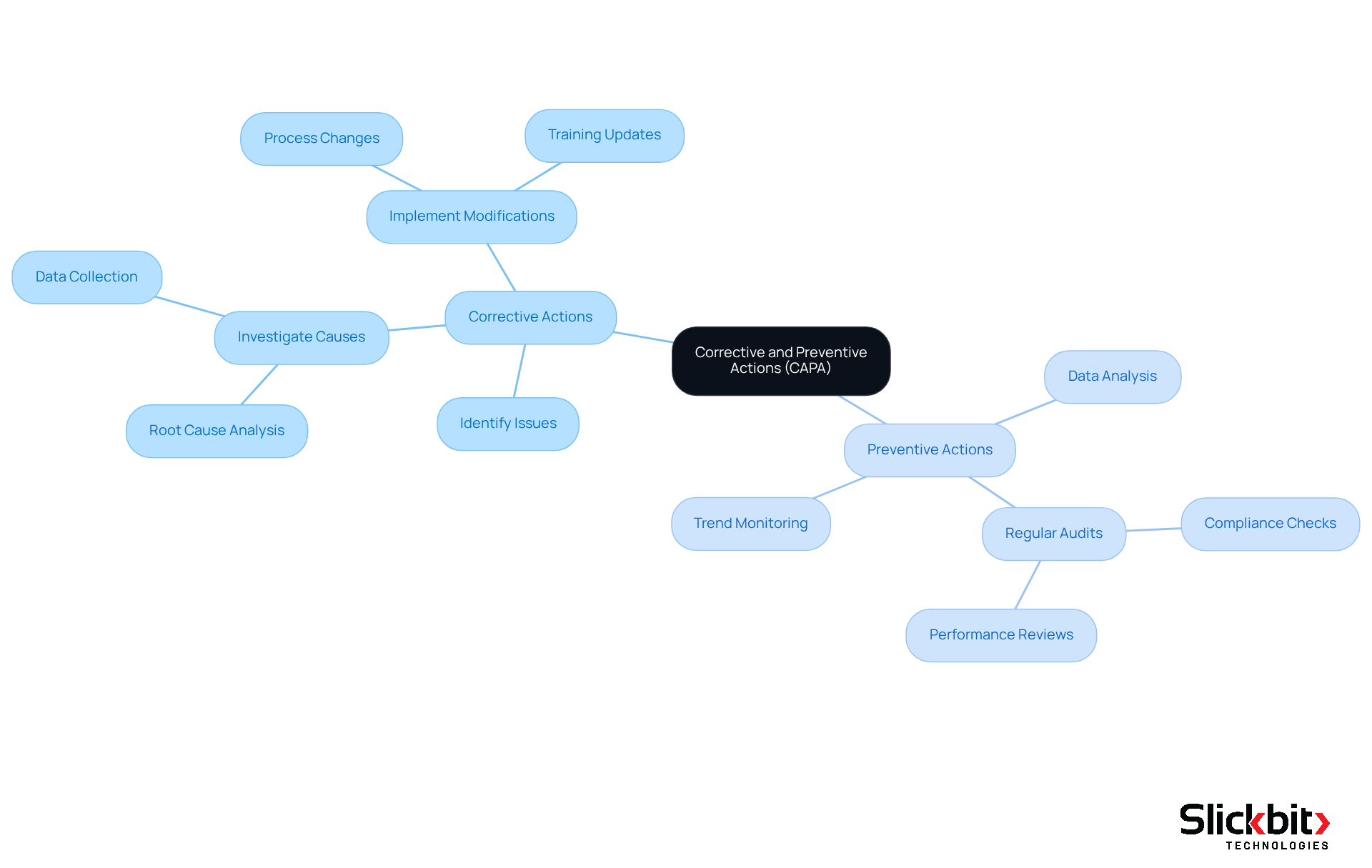
Define Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA)
Capa corrective action represents essential systematic approaches utilized by organizations, particularly in the life sciences sector, to identify, investigate, and resolve issues. Corrective measures specifically address issues that have already emerged, such as deviations from standard operating procedures or product flaws. These measures focus on eliminating the root causes of current problems to prevent their recurrence, thereby enhancing adherence and operational integrity.
Conversely, preventive actions are proactive measures designed to avert potential issues before they arise. This process involves meticulous data analysis and trend monitoring to identify risks at an early stage. By integrating both capa corrective action and preventive measures, organizations can effectively resolve existing issues while also establishing strategies to mitigate future risks, significantly bolstering overall quality and compliance.
The integration of AI technologies can further enhance CAPA procedures by identifying trends in systemic risks and recurrent violations stemming from FDA 483s. For instance, if a pharmaceutical company detects a batch of medication that has failed quality testing, the corrective action would involve investigating the root cause of the failure and implementing necessary modifications to the production process. Simultaneously, a preventive measure might entail instituting regular audits of the manufacturing process to proactively identify and address potential risks, thereby safeguarding against future quality failures. This dual strategy, augmented by AI insights, is crucial for maintaining industry standards and fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
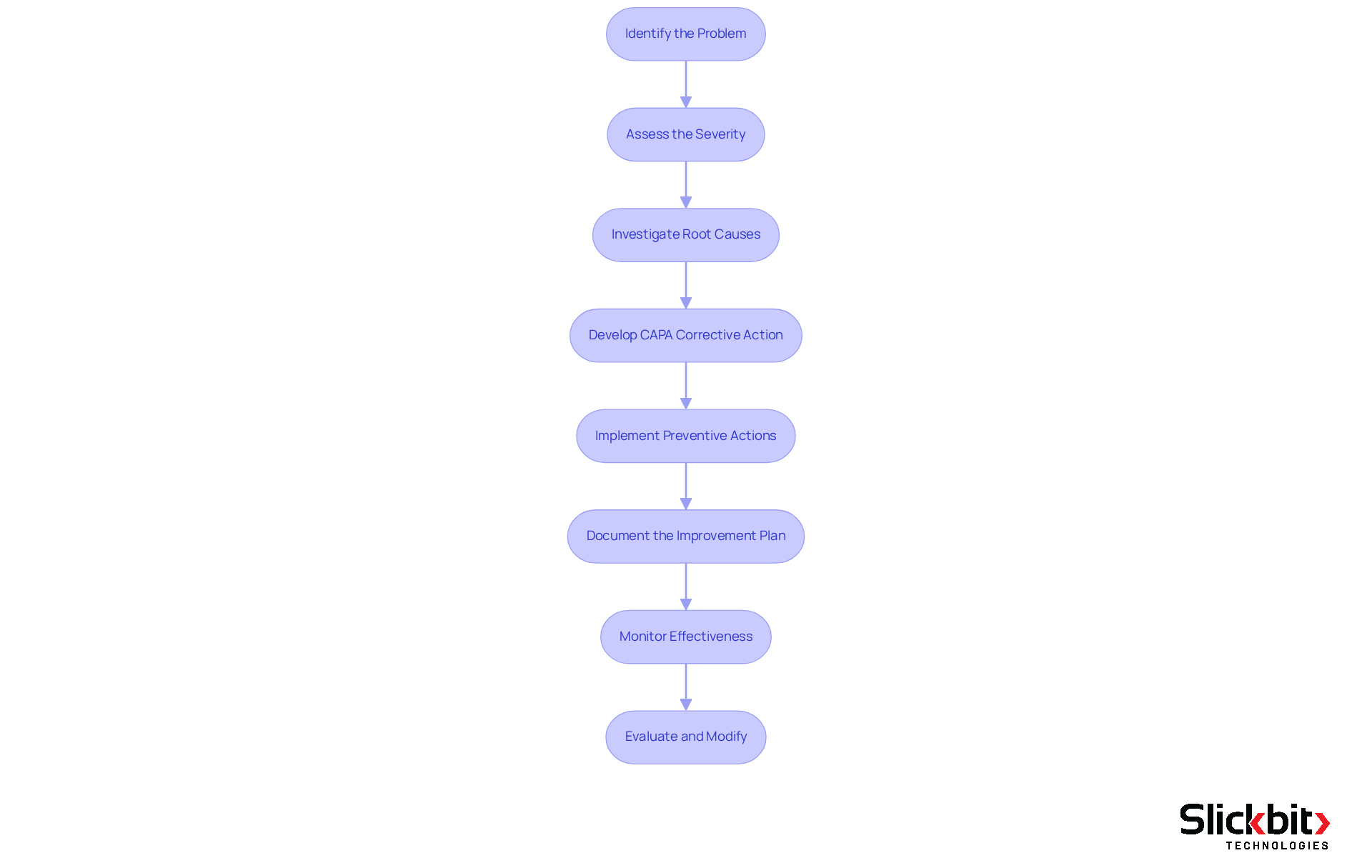
Develop a Step-by-Step CAPA Plan
To develop an effective CAPA plan, follow these essential steps:
-
Identify the Problem: Clearly define the issue at hand, which may include deviations from standard procedures, product defects, or any non-conformance requiring attention. Utilize data and reports to substantiate your identification.
-
Assess the Severity: Evaluate the impact of the problem on operations, compliance, and product quality. This evaluation assists in prioritizing the CAPA corrective action based on the severity of the issue, as unresolved problems can result in significant operational disruptions.
-
Investigate Root Causes: Conduct a thorough investigation to uncover the underlying causes of the problem. Employ techniques such as the 5 Whys or Fishbone Diagram to facilitate this analysis, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of contributing factors.
-
Develop CAPA Corrective Action: Based on the root cause analysis, outline specific, measurable steps to implement the identified corrective measures. Assign responsibilities to relevant team members to ensure accountability and clarity in execution.
-
Implement Preventive Actions: Identify and implement measures designed to prevent the recurrence of the issue. This may involve process modifications, additional staff training, or enhanced monitoring systems to safeguard against future non-conformance.
-
Document the Improvement Plan with CAPA Corrective Action: Create a formal document outlining the identified issue, root cause analysis, corrective and preventive measures, and timelines for execution. This documentation is essential for compliance with regulatory standards and serves as a reference for future audits. As noted by Larry Stevens, "Requests need to be documented and reviewed within a certain timeframe."
-
Monitor the effectiveness of the CAPA corrective action by closely observing the results after enacting the corrective action plan to confirm the efficacy of the actions taken. This may involve follow-up audits or reviews to assess whether the problem has been resolved and if preventive measures are functioning as intended. It's important to mention that "effectiveness checks for corrective and preventive actions may extend to weeks or months."
-
Evaluate and Modify: Consistently assess the system and implement required changes based on input and results. Ongoing enhancement is crucial for upholding adherence and excellence in operations, ensuring that the corrective and preventive action framework adapts to meet evolving regulatory requirements and operational obstacles. Involving a cross-functional team can improve the investigation, as it guarantees diverse viewpoints and accountability.
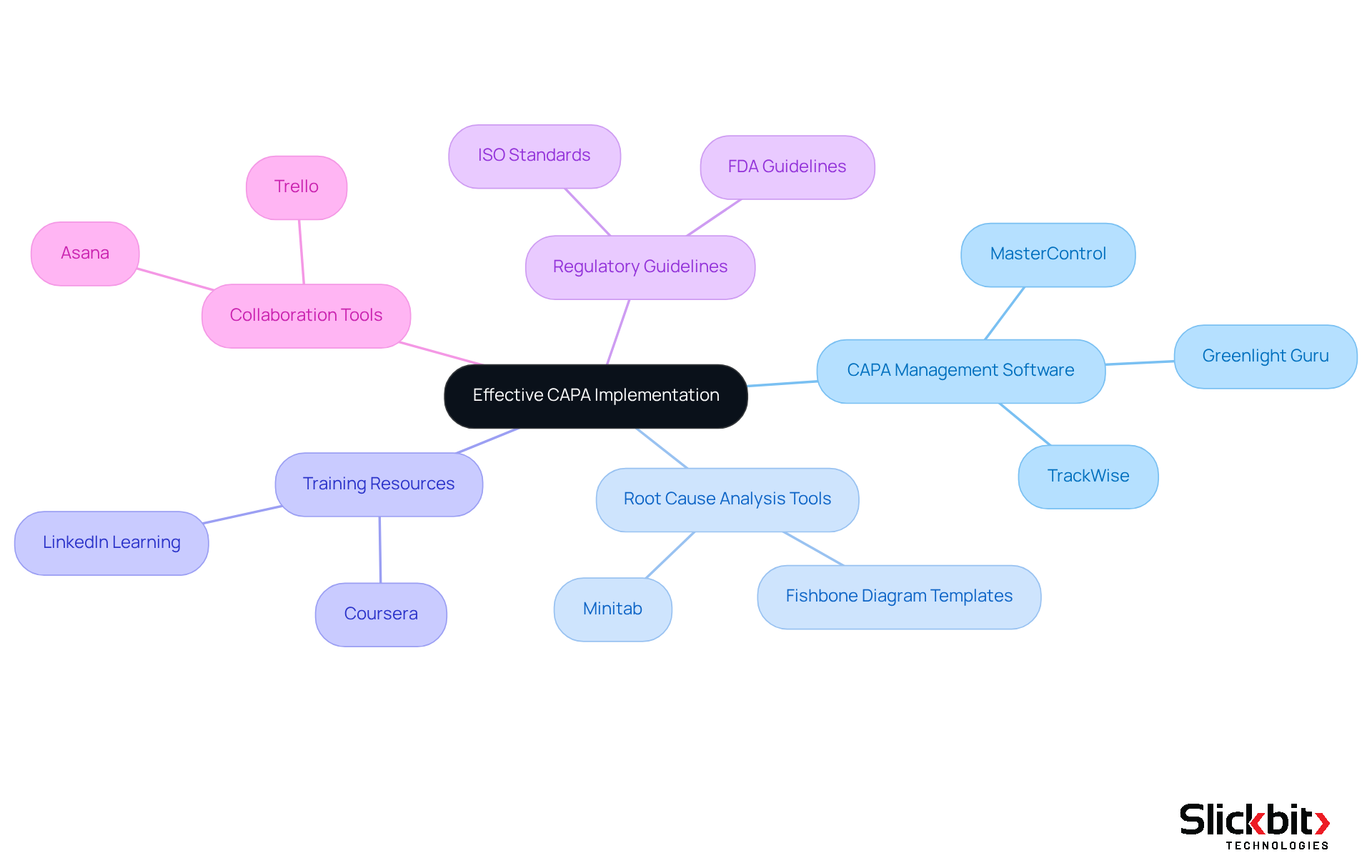
Tools and Resources for Effective CAPA Implementation
To effectively implement a capa corrective action plan, organizations should consider leveraging a suite of essential tools and resources that enhance both efficiency and compliance.
-
CAPA Management Software: Utilizing tools such as MasterControl, Greenlight Guru, or TrackWise can significantly optimize the corrective and preventive action workflow. These platforms automate documentation, monitor progress, and ensure adherence to regulatory standards, thereby streamlining the entire process.
-
Root Cause Analysis Tools: Employing software like Minitab or Fishbone Diagram templates is crucial for conducting thorough root cause analyses. These tools empower teams to identify underlying issues effectively, leading to more targeted solutions.
-
Training Resources: Investing in online courses and workshops focused on corrective and preventive action processes is vital for enhancing team knowledge and skills. Platforms such as Coursera or LinkedIn Learning provide relevant courses tailored specifically for Life Sciences professionals.
-
Regulatory Guidelines: It is imperative to familiarize oneself with guidelines from regulatory bodies, including the FDA and ISO standards related to corrective and preventive actions. These documents offer invaluable insights into regulatory requirements and best practices that are essential for compliance.
-
Collaboration Tools: Utilizing project management tools like Asana or Trello can facilitate effective communication and teamwork among group members involved in the CAPA process. This ensures that all participants are aligned and informed, fostering a collaborative environment.
By strategically utilizing these tools and resources, organizations can significantly improve their implementation of capa corrective action, ultimately resulting in enhanced compliance and superior quality outcomes.
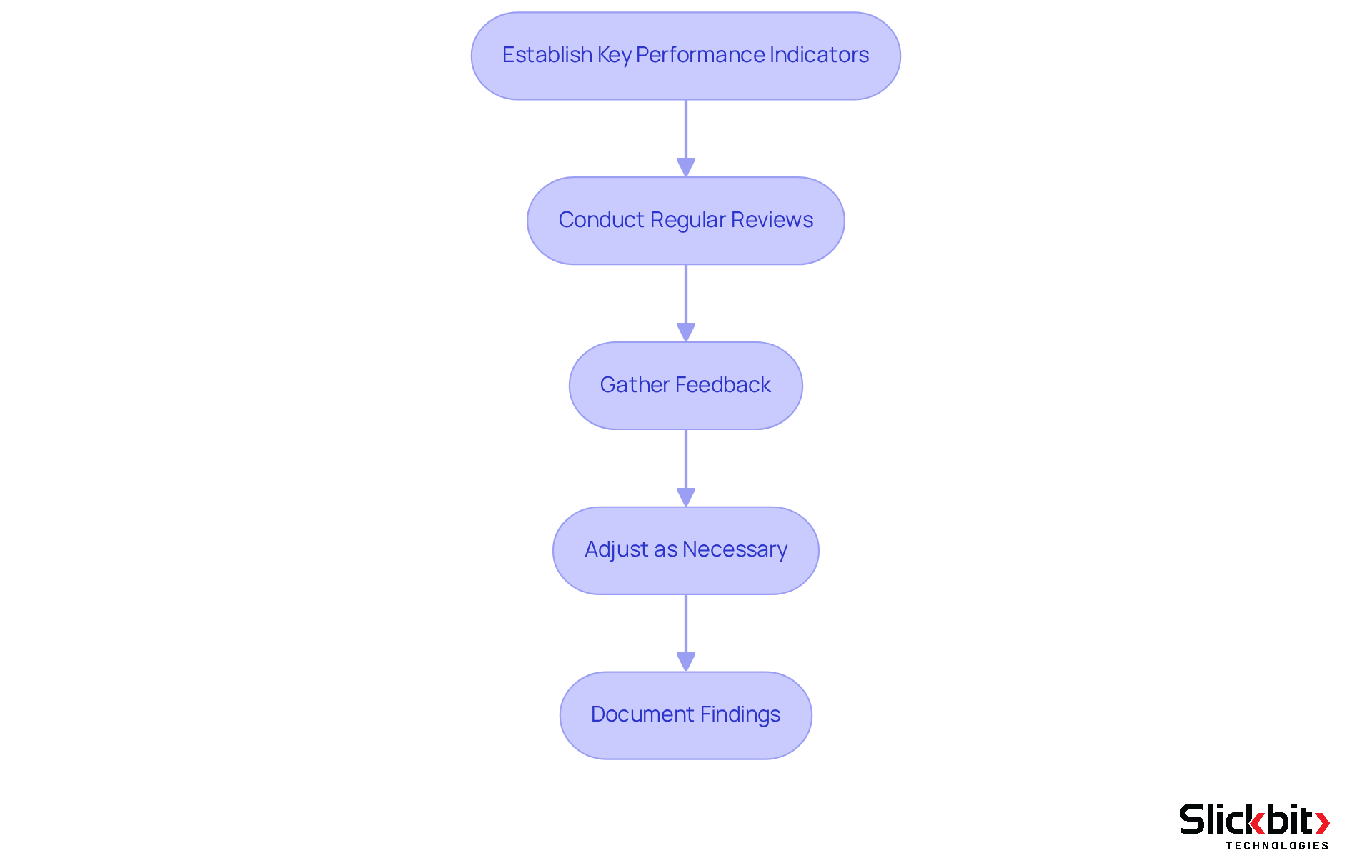
Monitor and Evaluate CAPA Effectiveness
To ensure the effectiveness of your CAPA plan, it is essential to implement the following monitoring and evaluation steps:
-
Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Define specific metrics to assess the effectiveness of your corrective and preventive actions. Common KPIs in Life Sciences include the frequency of recurring issues, average handling time for problem resolution, and compliance audit results. For instance, organizations that frequently assess their corrective and preventive actions report a 30% decrease in recurring problems, illustrating the significance of these metrics in fostering enhancements.
-
Conduct Regular Reviews: Arrange frequent evaluations of the corrective and preventive measures to assess whether the implemented steps are achieving the intended results. This may involve team meetings or audits to discuss progress, challenges, and any necessary adjustments. According to industry leaders, "Regular evaluations are essential for upholding compliance and ensuring that corrective measures are effective."
-
Gather Feedback: Collect insights from team members engaged in the corrective action and preventive action processes to identify areas for enhancement. Feedback can uncover the effectiveness of actions taken and highlight deficiencies in the method, fostering a collaborative approach to quality management. As pointed out by a prominent specialist, "Engaging team members in the feedback loop improves the corrective action and preventive action system and results in better outcomes."
-
Adjust as Necessary: Based on evaluation results and feedback, make required modifications to the corrective action plan. This may entail refining methods, enhancing training programs, or implementing additional preventive measures to address identified weaknesses.
-
Document Findings: Keep comprehensive records of the monitoring and evaluation process, including any modifications made to the action plan. Thorough documentation is crucial for adherence and serves as an important reference for future corrective and preventive actions.
By consistently observing and assessing the effectiveness of corrective actions, organizations can foster a culture of ongoing enhancement, ensuring that quality and regulatory standards are consistently met. Statistics show that organizations performing regular corrective and preventive action reviews experience a significant reduction in recurring issues, enhancing overall operational efficiency and compliance. Furthermore, specific KPIs such as the First Contact Resolution Rate (FCR) and Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT) are vital for assessing the success of CAPA initiatives in Life Sciences.
Conclusion
Mastering CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Actions) is crucial for organizations aiming for excellence in quality management, especially within the life sciences sector. By adopting a structured approach to identifying, investigating, and resolving issues, organizations can effectively tackle current challenges while proactively preventing future occurrences, thereby enhancing overall operational integrity.
This article presents a comprehensive step-by-step guide to developing an effective CAPA plan. Key elements encompass:
- Identifying the problem
- Assessing its severity
- Conducting root cause analysis
- Implementing corrective and preventive actions
- Continuously monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of these measures
The utilization of appropriate tools and resources, such as CAPA management software and root cause analysis tools, streamlines the process and ensures compliance with regulatory standards.
In conclusion, the importance of a robust CAPA framework cannot be overstated. By cultivating a culture of continuous improvement and employing strategic methodologies, organizations can enhance compliance and achieve superior quality outcomes. Embracing these practices will lead to greater operational efficiency and a more resilient organization, prepared to confront the challenges of the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does CAPA stand for, and what does it encompass?
CAPA stands for Corrective and Preventive Actions. It encompasses systematic approaches used by organizations, particularly in the life sciences sector, to identify, investigate, and resolve issues.
What are corrective actions in the context of CAPA?
Corrective actions are measures taken to address issues that have already occurred, such as deviations from standard operating procedures or product flaws. They focus on eliminating the root causes of current problems to prevent their recurrence.
What are preventive actions in the context of CAPA?
Preventive actions are proactive measures designed to prevent potential issues before they arise. This involves analyzing data and monitoring trends to identify risks early.
How do corrective and preventive actions work together in CAPA?
By integrating both corrective actions and preventive measures, organizations can effectively resolve existing issues and establish strategies to mitigate future risks, thereby enhancing overall quality and compliance.
How can AI technologies enhance CAPA procedures?
AI technologies can enhance CAPA procedures by identifying trends in systemic risks and recurrent violations, such as those stemming from FDA 483s. This can help organizations proactively address potential issues.
Can you provide an example of how CAPA is implemented in a pharmaceutical company?
If a pharmaceutical company detects a batch of medication that has failed quality testing, the corrective action would involve investigating the root cause of the failure and modifying the production process. Concurrently, a preventive measure might include instituting regular audits of the manufacturing process to identify and address potential risks proactively.
Why is the dual strategy of corrective and preventive actions important?
The dual strategy is crucial for maintaining industry standards and fostering a culture of continuous improvement, ensuring that organizations not only address current issues but also prevent future occurrences.


