Overview
The article titled "10 Essential Medical Abbreviations Every R&D Manager Should Know" addresses the critical need for R&D managers in the pharmaceutical sector to familiarize themselves with key medical abbreviations. Understanding these abbreviations is not merely beneficial; it is essential for ensuring effective communication and compliance within the intricate regulatory environment of drug development. By mastering this knowledge, R&D managers can navigate the complexities of their roles with greater confidence and authority. Consequently, this article serves as a vital resource for professionals aiming to enhance their operational effectiveness and uphold industry standards.
Introduction
In the fast-paced realm of pharmaceutical research and development, grasping key medical abbreviations is vital for R&D managers who aim for both efficiency and compliance. This article explores ten essential abbreviations that not only facilitate communication but also bolster the ability to navigate the intricate regulatory landscapes. As the industry undergoes rapid evolution, R&D managers must consider:
- How can they arm themselves with the right knowledge to tackle the challenges posed by stringent regulations and swift technological advancements?
Slickbit: AI Solutions for Regulatory Compliance in Pharmaceutical R&D
Slickbit.ai stands at the forefront of delivering AI-driven solutions that significantly enhance adherence to regulations in pharmaceutical R&D. By developing enterprise-level Minimum Viable Products (MVPs), Slickbit empowers R&D managers to automate adherence tasks, ensuring rigorous compliance with standards while boosting operational efficiency.
Noteworthy innovations, such as the AI-powered Regulatory Intelligence assistant, Lumino, provide teams with precise, traceable answers sourced from FDA and global guidance documents, allowing them to adeptly navigate the intricate regulatory landscape. Furthermore, Vault Redact automates the identification and removal of PII and PHI from documents, further supporting regulatory initiatives.
This not only accelerates the drug development process but also reduces the time-to-market for new therapies, highlighting the transformative impact of AI on regulatory practices within the life sciences sector. With the biologics market projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 15% until 2027, the importance of stringent regulatory adherence has never been more critical.
ICH: International Council for Harmonisation
The International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) serves a pivotal role in establishing guidelines that govern the pharmaceutical industry. These guidelines encompass critical aspects of drug development, including safety, efficacy, and quality. In 2025, a significant percentage of R&D managers reported awareness of ICH standards, underscoring their importance in ensuring that clinical studies and submissions align with international compliance expectations.
Adhering to these guidelines not only increases the likelihood of successful approvals but also streamlines the drug development process. Notably, successful drug development projects that comply with ICH guidelines have demonstrated improved outcomes, reflecting the standards' effectiveness in fostering innovation while prioritizing patient safety.
Industry leaders emphasize that comprehending ICH standards is essential for navigating the complexities of clinical studies and regulatory submissions, ultimately enhancing efficiency and compliance within the pharmaceutical landscape.
GCP: Good Clinical Practice
Good Clinical Practice (GCP) serves as a global ethical and scientific quality benchmark, essential for the design, execution, documentation, and reporting of clinical studies. R&D managers are pivotal in ensuring compliance with GCP, safeguarding the rights, safety, and well-being of study participants. Adhering to GCP not only bolsters the credibility of study data but also streamlines the regulatory approval process, underscoring a robust commitment to ethical research practices.
Recent updates to GCP standards, particularly the ICH E6(R3) guidelines, stress the integration of innovative study designs and digital health technologies, fostering a more patient-centric approach. These advancements are crucial as they enhance the effectiveness of clinical studies and promote participant involvement throughout the research lifecycle.
Furthermore, leveraging AI tools can significantly refine GCP regulations by identifying trends in systemic risks and ensuring adherence to ethical standards. AI can analyze data from FDA evaluations, providing insights that empower R&D managers to improve testing procedures and enhance compliance outcomes.
Expert opinions underscore the necessity of GCP compliance in clinical studies. For instance, adherence to GCP principles has been shown to correlate with improved study outcomes, ensuring that studies are both scientifically valid and ethically conducted. Statistics indicate that studies following GCP guidelines experience higher success rates in securing approvals, reinforcing the importance of these standards.
Ultimately, GCP transcends mere regulatory requirements; it constitutes a framework that guarantees participant safety and cultivates trust in clinical research. By prioritizing GCP adherence and exploring AI tools for compliance, R&D managers can markedly enhance the integrity and success of their clinical trials.
FDA: Food and Drug Administration
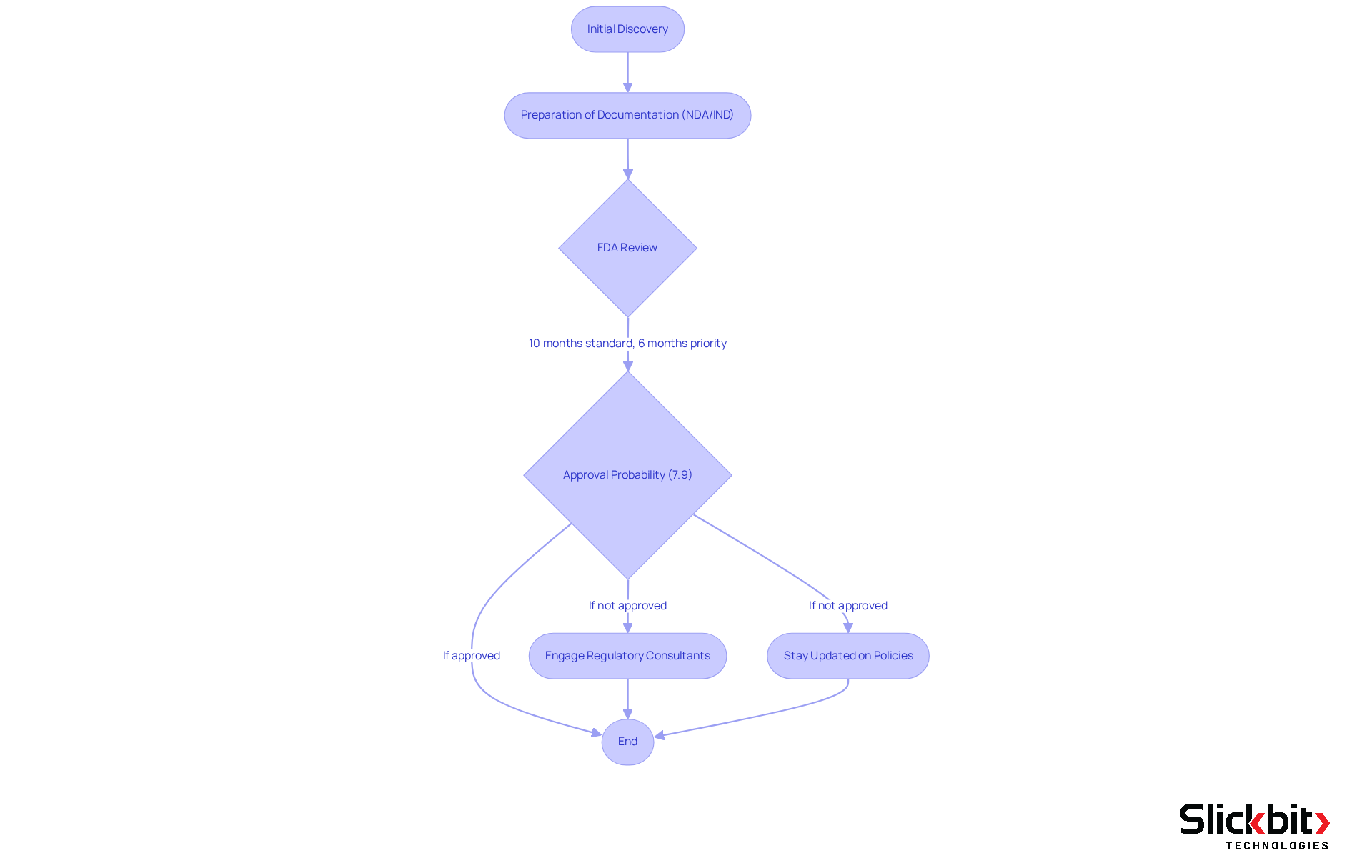
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a pivotal role in safeguarding public health by ensuring that drugs are both safe and effective. For R&D managers, a comprehensive understanding of FDA regulations, particularly the drug approval procedure, is essential for effectively navigating the complexities of introducing a new drug to the market. This process involves the meticulous preparation of extensive documentation for New Drug Applications (NDAs) and Investigational New Drug (IND) applications, which are crucial for obtaining official approval.
On average, it takes between 10 to 15 years for a drug to progress from initial discovery to approval by authorities, with the FDA typically reviewing NDAs within a standard timeframe of around 10 months. However, priority reviews can expedite this process to approximately 6 months. Despite these timelines, the likelihood of approval for drugs in Phase I development is only about 7.9%, underscoring the rigorous scrutiny that new drugs endure.
Navigating the FDA's requirements demands a proactive approach, which includes:
- Engaging with regulatory consultants
- Staying abreast of policy changes
Furthermore, effective communication with FDA reviewers can clarify expectations and mitigate unexpected challenges. As the landscape of drug development evolves, understanding these processes is vital for R&D managers aiming to successfully bring innovative therapies to market.
NDA: New Drug Application
A New Drug Application (NDA) represents the formal request submitted to the FDA for approval to market a new drug. R&D managers must ensure that their NDA submissions encompass comprehensive information regarding the drug's safety, efficacy, and production methods. A well-structured NDA, which conforms to the Common Technical Document (CTD) format, can significantly reduce the typical review timeline of 10 months. Moreover, expedited processes may shorten this duration to as little as 6 months for drugs qualifying for Priority Review.
Key components of a successful NDA include:
- Detailed clinical trial data
- Manufacturing quality assurance
- Adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP)
Best practices for preparing NDAs involve:
- Thorough documentation
- Proactive risk assessments
- Ensuring compliance with all regulatory requirements
By following these guidelines, R&D managers can facilitate a more seamless approval workflow, ultimately resulting in faster access to innovative treatments for patients in need.
IND: Investigational New Drug
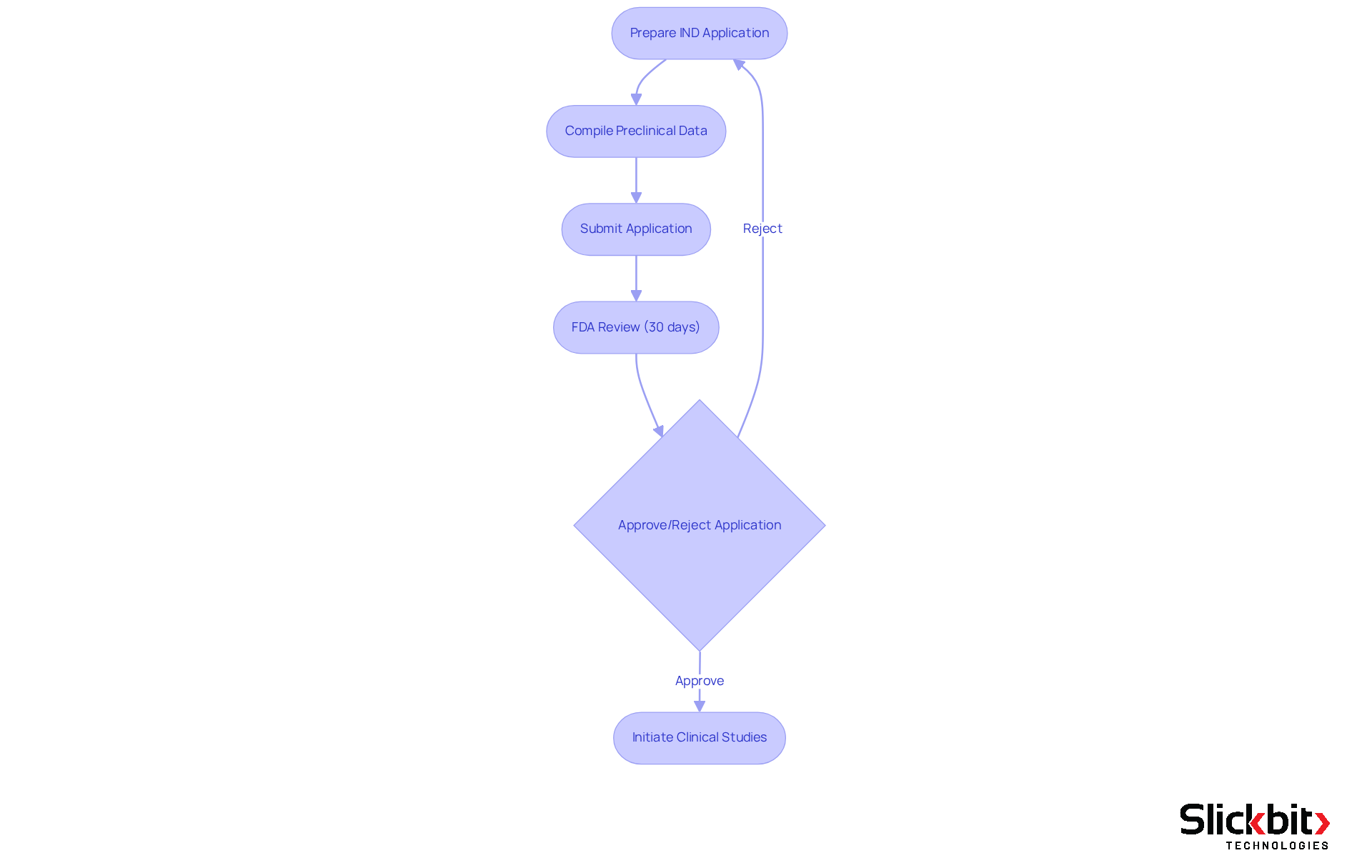
An Investigational New Drug (IND) application is a pivotal requirement for securing FDA authorization to administer investigational drugs to humans. R&D managers must navigate the IND process with meticulous attention, ensuring that all necessary preclinical data and study protocols are thoroughly prepared. This application is not just a formality; it is crucial for initiating clinical studies, as it must convincingly demonstrate the drug's safety for human testing.
Successful IND submissions not only facilitate the commencement of clinical studies but also significantly impact the overall drug development timeline, with the FDA typically reviewing applications within a 30-day window. The inclusion of comprehensive preclinical data, encompassing pharmacology and toxicology studies, is essential, as it establishes the foundation for future regulatory submissions and aids in mitigating risks associated with human trials.
Furthermore, leveraging AI technologies can assist R&D managers in identifying patterns in FDA inspections and compliance, thereby optimizing the IND workflow and enhancing operational efficiency. As industry specialists emphasize, the IND process represents a crucial stage in advancing new therapies, underscoring the importance of thorough preparation and strict adherence to FDA requirements.
CRO: Contract Research Organization
Contract Research Organizations (CROs) are integral to the success of pharmaceutical companies in navigating clinical trials and regulatory compliance. By collaborating with CROs, R&D managers tap into specialized expertise in vital areas such as:
- Patient recruitment
- Data management
- Regulatory submissions
This partnership not only boosts operational efficiency but also enables R&D teams to focus on their core research activities. Industry leaders underscore the importance of these collaborations, asserting that they significantly enhance efficiency and improve outcomes. Recent trends reveal an increasing dependence on CROs, with 87% of drug developers employing flexible service provider arrangements to streamline their clinical development initiatives. Successful partnerships between pharmaceutical firms and CROs have demonstrated notable improvements in study efficiency, further emphasizing the critical role of these strategic alliances in managing the complexities of drug development.
SOP: Standard Operating Procedure
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are essential documented processes that delineate the necessary steps for executing specific tasks in clinical research. R&D managers must implement SOPs for all critical activities, including:
- Trial design
- Data collection
- Reporting
Following these procedures not only promotes consistency and quality in research but also improves adherence to guidelines, significantly reducing the risk of violations during audits. Furthermore, effective SOP development is crucial; organizations that prioritize clear, concise SOPs often report improved operational efficiency and reduced errors. Recent insights from regulatory experts emphasize that strong SOP adherence is a cornerstone of successful conformity in pharmaceutical R&D, ensuring that all team members are aligned with best practices and regulatory mandates.
CAPA: Corrective and Preventive Action
Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA) serves as a critical framework for identifying, investigating, and addressing regulatory challenges within the pharmaceutical sector. R&D managers bear the responsibility of implementing robust CAPA systems to swiftly address any deviations from established protocols. This systematic approach not only mitigates immediate regulatory risks but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement, significantly enhancing the organization's overall compliance posture.
Notably, studies indicate that companies utilizing automated CAPA management achieve an impressive adherence rate of 99%, compared to just 85% for those relying on manual processes. Furthermore, effective CAPA procedures are indispensable in clinical trials, where maintaining compliance is essential to safeguarding data integrity and patient safety.
By prioritizing CAPA, organizations can not only resolve current issues but also proactively avert future occurrences, thereby protecting their reputation and operational efficiency in a highly regulated environment.
QMS: Quality Management System
A Quality Management System (QMS) is essential for establishing the organizational structure, processes, and procedures that guarantee quality in pharmaceutical development. R&D managers must prioritize a robust QMS to meet regulatory standards and enhance operational efficiency. By incorporating quality management principles into their workflows, organizations can significantly enhance product quality and ensure adherence to evolving regulations.
Furthermore, leveraging AI tools like Slickbit's Trend 483 can further enhance this process by identifying trends in systemic risks and repeat violations from FDA 483s. Trend 483 allows R&D managers to search, filter, and view complete FDA 483s directly, offering deeper insights that facilitate proactive adherence management. Companies utilizing such AI-driven insights have reported notable improvements in operational efficiency and a reduction in compliance issues, reinforcing the value of integrating advanced technology into quality management practices.
Conclusion
Understanding essential medical abbreviations is crucial for R&D managers in the pharmaceutical sector. Mastery of these terms not only streamlines communication but also enhances compliance with regulatory standards, thereby improving the overall efficiency of drug development processes. As the industry continues to evolve, staying informed about these abbreviations and their implications is paramount for success.
The article highlights ten key medical abbreviations that play a significant role in regulatory compliance and drug development:
- International Council for Harmonisation (ICH)
- Good Clinical Practice (GCP)
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
Each abbreviation encapsulates critical guidelines and processes that R&D managers must navigate. Furthermore, leveraging AI solutions, such as those provided by Slickbit, empowers managers to adhere to these standards, ensuring that their teams can focus on innovation while maintaining compliance.
In a landscape where regulatory adherence is becoming increasingly complex, R&D managers are encouraged to prioritize the mastery of these abbreviations and their corresponding guidelines. By doing so, they not only enhance their operational efficiency but also contribute to the advancement of safe and effective therapies for patients in need. Embracing these essential tools and insights will ultimately pave the way for more successful drug development initiatives in the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Slickbit and what solutions does it provide for pharmaceutical R&D?
Slickbit is a company that delivers AI-driven solutions to enhance regulatory compliance in pharmaceutical research and development (R&D). It develops enterprise-level Minimum Viable Products (MVPs) that automate adherence tasks, improving compliance with regulations and operational efficiency.
What is Lumino and how does it assist R&D teams?
Lumino is an AI-powered Regulatory Intelligence assistant developed by Slickbit. It provides teams with precise, traceable answers from FDA and global guidance documents, helping them navigate the complex regulatory landscape effectively.
How does Vault Redact contribute to regulatory compliance?
Vault Redact automates the identification and removal of Personally Identifiable Information (PII) and Protected Health Information (PHI) from documents, supporting regulatory initiatives and enhancing compliance efforts.
What impact does AI have on the drug development process?
AI accelerates the drug development process and reduces the time-to-market for new therapies, demonstrating a transformative effect on regulatory practices within the life sciences sector.
What role does the International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) play in pharmaceutical R&D?
The ICH establishes guidelines that govern the pharmaceutical industry, covering critical aspects of drug development such as safety, efficacy, and quality. Compliance with ICH standards is vital for aligning clinical studies and submissions with international regulations.
Why is adherence to ICH guidelines important for R&D managers?
Adhering to ICH guidelines increases the likelihood of successful drug approvals and streamlines the drug development process. Compliance has been shown to improve outcomes in drug development projects.
What is Good Clinical Practice (GCP) and why is it significant?
Good Clinical Practice (GCP) is a global ethical and scientific quality benchmark essential for the design, execution, documentation, and reporting of clinical studies. It safeguards the rights and well-being of study participants and enhances the credibility of study data.
How have recent updates to GCP standards impacted clinical studies?
Recent updates, particularly the ICH E6(R3) guidelines, emphasize integrating innovative study designs and digital health technologies, fostering a more patient-centric approach that enhances the effectiveness of clinical studies.
How can AI tools enhance GCP compliance?
AI tools can identify trends in systemic risks and ensure adherence to ethical standards by analyzing data from FDA evaluations, providing insights that help R&D managers improve testing procedures and compliance outcomes.
What is the overall importance of GCP compliance in clinical trials?
GCP compliance is essential for ensuring participant safety, enhancing the integrity of clinical trials, and cultivating trust in clinical research. Studies that adhere to GCP principles tend to have higher success rates in securing approvals.

